Dispersion modelling: agriculture: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
*[http://www.src.com/calpuff/calpuff1.htm CALPUFF modeling system] | *[http://www.src.com/calpuff/calpuff1.htm CALPUFF modeling system] | ||
{{IEHIAS}} | |||
Latest revision as of 20:13, 25 September 2014
- The text on this page is taken from an equivalent page of the IEHIAS-project.
As part of the EU-funded INTARESE project, which contributed to the development of this Toolbox, a case study was carried out to assess the health effects of agricultural land use change in two study areas, in Greece and England.
In the Greek study area, in Thessalia and Central Macedonia, dispersion modelling was used to assess exposures to pesticides, particulate matter, endotoxins and pollen generated by agricultural activities, under a baseline and two policy scenarios (for the years 2020 and 2050). A Eulerian box-volume model was used for this purpose.
Methodology
Yearly average meteorological data (wind speed and direction, temperature, relative humidity) from 6 meteorological stations were used as input to CALMET meteorological model to estimate the mixing layer height (H) and the magnitude of wind velocity (U) for 4 x 4 km grid across the study areas. The box volume model was then run to estimate pollutant concentrations in each of the 4 x 4 km cells for the entire area of study, using the simple formula:
where:
C = pollutant concentration in air (g/m3)
E = emission of pollutant (g/sec)
U = wind velocity (m/s)
H = mixing layer height (m)
L = lateral “box” dimension (m)
This simple method provides first reasonable estimates, useful for comparison with the more detailed calculations done using alternative modelling techniques (see Focal sum modelling: agriculture).
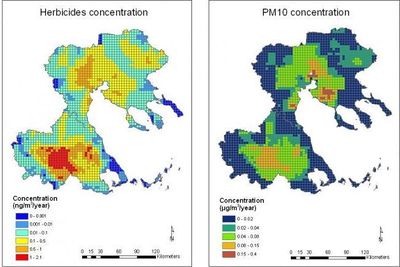
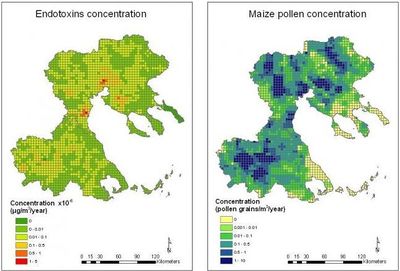
Modelled concentrations of herbicides, PM10, endotoxins and pollen (from maize) for the baseline year 2000 in Thessaly and C. Macedonia are illustrated in FIgures 1 and 2.