Route modelling for IEHIAS: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "Category:IEHIAS :''The text on this page is taken from an equivalent page of the IEHIAS-project. File:routemodellingiehias.png|thumb|400px|Figure 1: Exa...") |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
When running the script the user will be asked to define the network, origin and destination data. The end result is a shapefile with shortest paths routes between every origin and destination locations along the road network (see Figure 1). | When running the script the user will be asked to define the network, origin and destination data. The end result is a shapefile with shortest paths routes between every origin and destination locations along the road network (see Figure 1). | ||
==See also== | |||
{{IEHIAS}} | |||
Latest revision as of 20:08, 25 September 2014
- The text on this page is taken from an equivalent page of the IEHIAS-project.
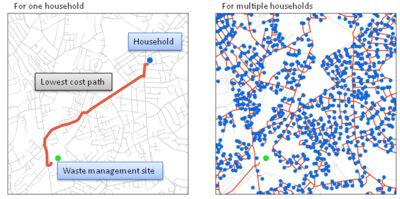
The route model simulates routes between an origin (e.g. a household) and a destination (a waste management site). At its simplest, this can be done just by finding the shortest distance between the two. More realistically, the model can allow for differences in the cost of travelling along each route - for example, depending on traffic speed, road tolls or other barriers. Here, different cost weights were assigned to different road types.
Modelling is done in ArcGIS. An ArcView3.2 script, which can be downloaded from the ESRI website, is used to perform this analysis. The script needs the following geographical information in order to perform the route modelling:
- Network data: digital road network
- Origin data: postcodes (or other population centroids) with information of population or household numbers
- Destination data: waste management sites (e.g. waste transfer stations, incinerators, landfill sites).
When running the script the user will be asked to define the network, origin and destination data. The end result is a shapefile with shortest paths routes between every origin and destination locations along the road network (see Figure 1).