Expert elicitation methodology: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "Category:IEHIAS Category:Assessment design :''The text on this page is taken from an equivalent page of the IEHIAS-project. There are many ways to dea...") |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
[[Image:expert_elicitation_protocol_steps.png]] | [[Image:expert_elicitation_protocol_steps.png]] | ||
==References== | |||
* Anne B Knol , Pauline Slottje, Jeroen P van der Sluijs and Erik Lebret. [http://www.ehjournal.net/content/9/1/19 The use of expert elicitation in environmental health impact assessment: a seven step procedure.] Environmental Health 2010, 9:19doi:10.1186/1476-069X-9-19 | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| Line 16: | Line 20: | ||
* {{#l:Health Effects Methodology.pdf}} | * {{#l:Health Effects Methodology.pdf}} | ||
{{IEHIAS}} | |||
Latest revision as of 18:49, 14 October 2014
- The text on this page is taken from an equivalent page of the IEHIAS-project.
There are many ways to deal with uncertainties or inadequacies in information. One of these is expert elicitation. Expert elicitation involves: “the structured questioning of experts on a subject about which knowledge in unavailable, incomplete or controversial”
Expert elicitation can be a useful means to provide a temporary summary of the limited available knowledge. This summary of knowledge can help to make decisions about how to scope an issue that is being considered for assessment, how to design the assessment (and whether or not a full assessment is warranted), to clarify and confirm assumptions or causal models, and to estimate important parameters (e.g. exposure-response functions) needed for the analysis. It can also also serve as a provisional basis for policy until further research has been carried out.
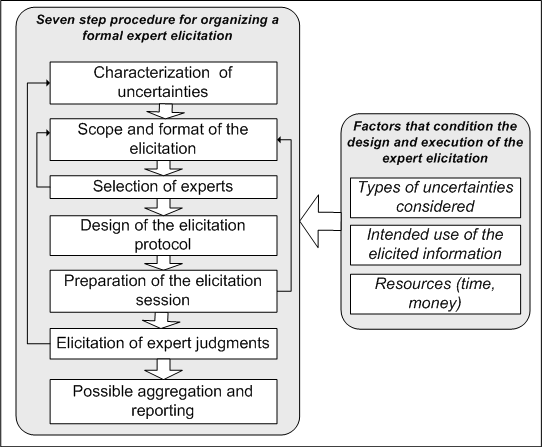
To ensure consistency, it is useful to organise expert elicitations using a clear protocol which outlines the specific steps that need to be taken. A protocol for this purpose is attached below, and the approach is summarised in the paper listed under References. This takes a deliberately broad perspective on the use of expert elicitation. The seven steps outlined in this protocol are presented in the figure below.
References
- Anne B Knol , Pauline Slottje, Jeroen P van der Sluijs and Erik Lebret. The use of expert elicitation in environmental health impact assessment: a seven step procedure. Environmental Health 2010, 9:19doi:10.1186/1476-069X-9-19