Climate change policies in Helsinki
| Moderator:Jouni (see all) |
|
|
| Upload data
|
- This assessment was used for training in Decision analysis and risk management 2015 course. To see student contributions, see a previous version.
Scope
Question
What is the energy need of buildings in Helsinki and the related greenhouse gas emissions and health impacts? How can these be affected by renovation of buildings and fuel changes in district heating?
Intended use and users
A problem in the climate policy practices in the City of Helsinki is that there is not enough information about different costs and impacts of different climate change mitigation measures, especially in the long term. This is slowing down the decision-making process. The results of this course will be used at the City of Helsinki Environment Centre to assess the outcomes of different ways to reduce GHG emissions. The results will help in identifying the most favourable ways to cut GHG emissions.
Participants
- Jouni Tuomisto (THL), the coordinator of the assessment
- The participants of the Decision analysis and risk management 2015 course.
- Helsinki Environment Centre
- Siemens and the City Performance Tool experts
Boundaries
- Time: 2010-2060
- Spatial: the city of Helsinki
Decisions and scenarios
Energy saving policy: Relates to the shares of efficiency types when new buildings are built (ovariable efficiencyShares).
- BAU: Business as usual, no change to the energy efficiency of buildings.
- Energy saving moderate: No change to the energy efficiency of buildings.
- Energy saving total: Starting from the year 2020 buildings are built to be more energy efficient. 25 percentage points of production shifts from low-energy buildings to passive buildings. Starting from the year 2040 another 10 percentage points of production shifts from low-energy to passive.
Fuel policy: Helen increases the share of wood-based biofuels used in Hanasaari and Salmisaari power plants to 40 % of fuels used. Both burn 40 % wood pellets and 60 % coal. (ovariable fuelShares)
- BAU: Business and usual, both power plants continue burning only 5-10 % biofuel.
- 40 bio: Shift to biofuels, starting from the year 2020 the share of wood-based fuels increase by 24 percentage points and coal's share decrease by the same amount.
Energy saving policy (ovariable renovationRate)
- BAU: Business as usual, every year 1 % of all buildings over 30 years old are renovated to increase their energy efficiency.
- Energy saving moderate: Increased energy renovation, every year 2 % of all buildings over 30 years old are renovated to increase their energy efficiency.
- Energy saving total: Greatly increased energy renovation, every year 3 % of all buildings over 30 years old are renovated to increase their energy efficiency.
See also decisions in Climate change policies and health in Kuopio.
| Show details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Timing
The data will be collected before the end of the Decision analysis and risk management 2015 course (12th May, 2015). The model runs will be finalised soon after that. Results will be available before September 2015.
Answer
Results
Conclusions
Rationale
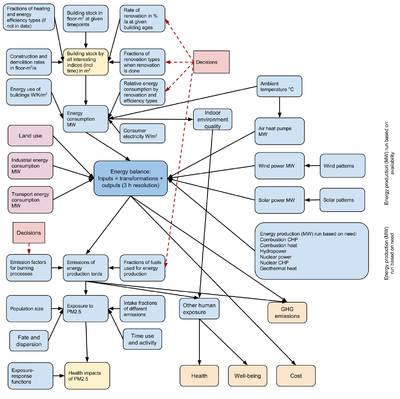
Stakeholders
- City of Helsinki
Dependencies
- Building stock in Helsinki
- Energy use of buildings
- Emission factors for burning processes
- Climate change policies and health in Kuopio#Direct inputs
- District heating production units in Helsinki metropolitan area
- Exposure to PM2.5 in Finland
- OpasnetUtils/Drafts
- Health impact assessment
- Disease risk
- Exposure-response function
- Burden of disease in Finland
- Outdoor air temperature in Finland
- Unit price of carbon emission permits
- Data files
 Climate policies Helsinki data
Climate policies Helsinki data Climate policies Helsinki additional data
Climate policies Helsinki additional data Helsingin_rakennuskanta_Facta_ajo_huhtikuu_2015
Helsingin_rakennuskanta_Facta_ajo_huhtikuu_2015- Additional sources of information (may be useful)
- Motiva, Sami Seuna [1]
- Tilastokeskus Jonna Hakala 09 1734 3419, energia@tilastokeskus.fi [2]
- VTT: Energy efficiency scenarios of buildings (2014) [3]
- VTT energy efficiency expert Jyri Nieminen
- Tampere University of Technology: EPAT: Energy saving potential in Finnish housing stock by 2050. [4] See especially section 4.2.4.
Discussions
These are some resolutions of discussions within the assessment.
- City level climate change mitigation is not useless although international treaties are important for success.D↷
- Climate change adaptation is not more important than mitigation on city level.R↻
- Citizens may have a key role in implementing city climate policies.D↷
- Food issues are underrepresented in climate discussions although food is a major emission source.R↻
- The role of district heating by nuclear energy in Helsinki is unclear.D↷
- There may be large uncertainty in CO2 emission factors of biofuels.D↷
Analyses
Indices
The data will be classified according to these indices:
- Building: Residential, Public, Industrial, Other. For separating different use purposes of buildings.
- Constructed: Years of construction of the buildings in the format 1990-1999, 2000-2009, 2010-2013.
- Heating: District, Electricity, Geothermal, Oil, Wood,
The results of each ovariable will be measuring these things:
- buildings: total floor area in m2.
Calculations
- Model run 15.6.2015
- Model run 24.6.2015 (new structure of building model)
⇤--#: . In the results the graph "Energy used in heating in Helsinki" shows a twice or thrice bigger energy use for Oil and Other than the table "Total energy consumption in Helsinki in 2013 (GWh)" on Helsinki energy consumption would suggest. --Heta (talk) 08:18, 11 June 2015 (UTC) (type: truth; paradigms: science: attack)
⇤--#: . Effective floor area of buildings by building type -table on page Building stock in Helsinki has the current building stock at 7 million m2 more than the graphs in the result, and the future estimates are even more higher than the code result estimates --Heta (talk) 10:49, 11 June 2015 (UTC) (type: truth; paradigms: science: attack)
See also
- Other related assessments
- Climate change policies and health in Kuopio
- Climate change policies in Basel
- Climate change policies in Kuopio
- Helsinki Region Infoshare
Other variables and pages to look at
- Thermal energy need in Helsinki Metropolitan Area
- Heating consumption of buildings
- Emission assessment of small-scale energy production in the Helsinki metropolitan area
- CLAIH assessment
- BIOHER assessment
- Unit heat consumption of buildings in Finland
 Assessment of small-scale energy production in Helsinki Metropolitan area
Assessment of small-scale energy production in Helsinki Metropolitan area Bioher model
Bioher model Claih model
Claih model Housing stock in Helsinki metropolitan area
Housing stock in Helsinki metropolitan area Parameters, gabi-model
Parameters, gabi-model- Gabi 4.3 - life cycle assessment software
- Energiaremontti
- Halme et al. 2014 Kasvua ja työllisyyttä uudella energiapolitiikalla
- Energiaremontti 2015 -Facebook-ryhmä
- Uusi energiapolitiikka -Facebook-sivu
- Helsingin Sanomat: Energiavallankumous horjuttaa Helsingin jättivoimalahanketta – miljardin euron päätöstä saatetaan lykätä jälleen
- Possibly useful variables
- Assessment on impacts of emission trading on city-level (ET-CL)
- Exposure of Finnish subpopulations to fine particles due domestic wood combustion
- Prices of fuels in heat production
- Heating consumption of buildings
- Value of a life year (VOLY)
- Unit price of energy in residential heating in Finland
- Unit value of restricted activity days (RADs)
- Unit value of hospital admissions
- Value of a statistical life (VSL)
- Duration of morbidity
- Disability weights
- Morbidity in Finland LOOK AT THE ANALYTICA FILE
- Mortality in Finland
- Population of Finland
- Asthma prevalence
- Breathing rate
- Mortality in Finland
- Electricity production in Finland
- District heat production in Finland
- heande:HI:Policy for PM2.5 Exposure (ASK LAMA IF THIS CAN BE RELEASED!
- ERF for cold exposure and mortality
- ERF for heat exposure and morbidity
- ERF of ambient temperature on mortality
- ERF of indoor dampness on respiratory health effects
- Exposure to dampness and mold contamination in homes in Finland
- ERF for short term PM10 exposure and lower respiratory symptoms (LRS)
- ERF for short term PM10 exposure and medication usage by people with asthma
- ERF for short term PM2.5 exposure and minor restricted activity days (MRADs)
- ERF for short term PM2.5 exposure and work loss days (WLDs)
- ERF for short term PM2.5 exposure and restricted activity days (RADs)
- ERF for short term PM10 exposure and respiratory hospital admissions
- ERF for short-term PM10 exposure and cardiovascular hospital admissions
- Concentration-response to PM2.5 THIS IS THE NEWEST but many pages should be merged with this. RENAME?
- Exposure to PM2.5 in Finland
- PM 2.5 concentration indoors from indoor sources in Finland THIS IS A METHOD
- PM infiltration from outdoor air to indoor air THIS IS A METHOD
- N2O emissions from house stock heating in Finland
- CH4 emissions from house stock heating in Finland
- CO2 emissions from house stock heating in Finland
- Unit heat consumption of buildings in Finland
- Energy efficiency of buildings in Finland THIS IS ACTUALLY BUILDING STOCK OF FINLAND
- Heating systems in buildings in Finland SHOULD BE UPDATED FROM STAT FINLAND IF NEEDED
- Almost empty pages that should be removed
- Unit price of carbon emission permits
- Outdoor air temperature in Finland
- PM2.5 concentration in Finland
- PM2.5 emissions from house stock heating in Finland
- New house stock production in Finland
Keywords
Helsinki, energy, building stock, heating, renovation.
References