Benefit-risk assessment on farmed salmon: Difference between revisions
(→Definition: imagemap added to the causal diagram) |
(Result legends improved) |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
===Purpose=== | ===Purpose=== | ||
'''The purpose''' of the assessment is to evaluate the recommendation given by Hites et al <ref>R. A. Hites et al. Global assessment of organic contaminants in farmed salmon. Science, 9 Jan. 2004, p. 226</ref> that people should not eat farmed salmon too often because of the pollutant concentrations. | '''The purpose''' of the assessment is to evaluate the recommendation given by Hites et al <ref name=hites>R. A. Hites et al. Global assessment of organic contaminants in farmed salmon. Science, 9 Jan. 2004, p. 226</ref> that people should not eat farmed salmon too often because of the pollutant concentrations. | ||
===Boundaries=== | ===Boundaries=== | ||
| Line 69: | Line 69: | ||
The main results and conclusions have been published by Tuomisto et al.<ref>Tuomisto JT, Tuomisto J, Tainio M, Niittynen M, Verkasalo P, Vartiainen T, Kiviranta H, Pekkanen J. Risk-benefit analysis of eating farmed salmon. Science. 2004 Jul 23;305(5683):476-7 [http://www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/305/5683/476 Read the article]</ref> | The main results and conclusions have been published by Tuomisto et al.<ref>Tuomisto JT, Tuomisto J, Tainio M, Niittynen M, Verkasalo P, Vartiainen T, Kiviranta H, Pekkanen J. Risk-benefit analysis of eating farmed salmon. Science. 2004 Jul 23;305(5683):476-7 [http://www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/305/5683/476 Read the article]</ref> | ||
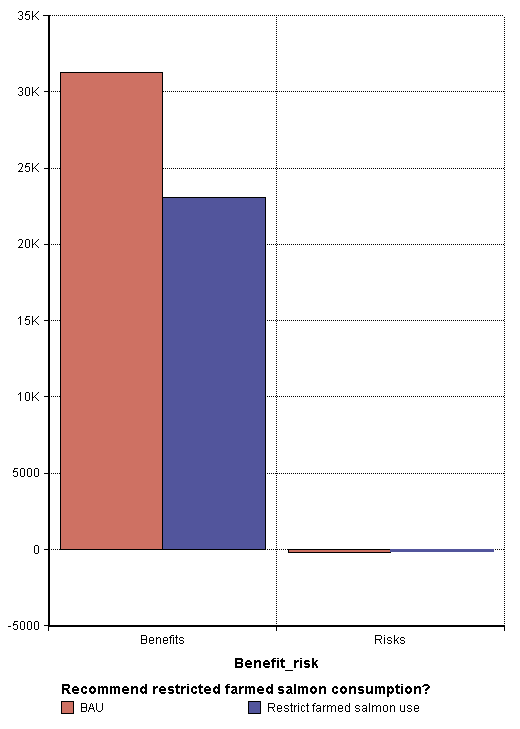
Figure. Benefits and risks (number of avoided deaths per year) of eating farmed salmon in Western Europe. | |||
[[Image:Benefit-risk diagram for farmed salmon.PNG]] | [[Image:Benefit-risk diagram for farmed salmon.PNG]] | ||
Table: Net health impacts of eating farmed salmon. The results include the health impacts of the total health impact of omega-3 intake from salmon. | Table: Net health impacts (avoided deaths per year) of eating farmed salmon in Western Europe. The results include the health impacts of the total health impact of omega-3 intake from salmon. | ||
{| {{prettytable}} | {| {{prettytable}} | ||
| Line 149: | Line 150: | ||
|} | |} | ||
Table: Net health impacts of eating farmed salmon compared with the business-as-usual scenario. | Table: Net health impacts (avoided deaths per year) of eating farmed salmon in Western Europe, compared with the business-as-usual scenario. The results include the health impacts of the total health impact of omega-3 intake from salmon. | ||
{| {{prettytable}} | {| {{prettytable}} | ||
| Line 226: | Line 226: | ||
|---- | |---- | ||
|} | |} | ||
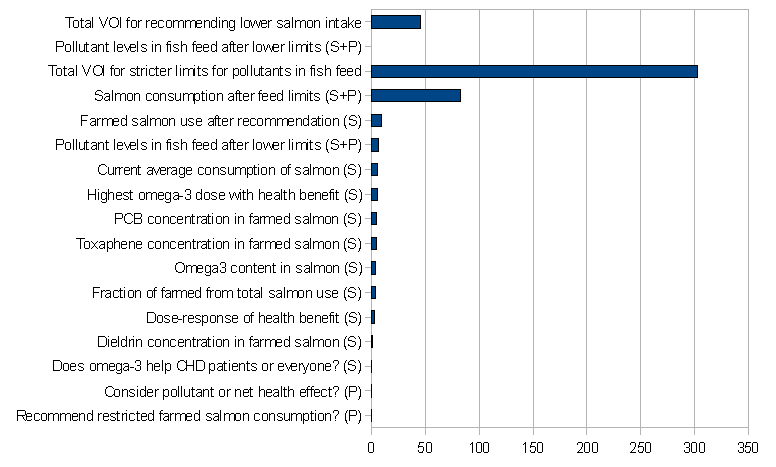
Figure. Value of information (VOI) calculated as avoided deaths per year in Western Europe. The first two bars are for the decision about recommending restrictions to salmon consumption. No single variable was important enough to gain any VOI; therefore, only the uncertain variable emphasized by Hites<ref name=hites>R. A. Hites et al. Global assessment of organic contaminants in farmed salmon. Science, 9 Jan. 2004, p. 226</ref> is shown. The other bars are for the decision about setting stricter limits for fish feed. | |||
[[Image:VOI analysis for farmed salmon.PNG]] | [[Image:VOI analysis for farmed salmon.PNG]] | ||
Revision as of 11:08, 2 January 2008
Scope
Purpose
The purpose of the assessment is to evaluate the recommendation given by Hites et al [1] that people should not eat farmed salmon too often because of the pollutant concentrations.
Boundaries
- Pollutants: Toxaphene, dieldrin, PCB
- Nutrients: Omega-3 fatty acids
- Health impacts:
- Total cancer caused by pollutants
- Cardiovascular deaths and the impact of omega-3 fatty acids
- Population: the population of Western Europe (European Economic Area as of beginning of 2004)
- Current situation (year 2004)
Scenarios
- Recommendation for not to eat farmed salmon too often (yes/no)
- Setting up new stricter regulations about pollutants in fish feed (yes/no)
Intended users
- The primary users are public health authorities and decision-makers involved in giving food recommendations.
- The secondary user group is the general public. Quantitative estimates are offered to increase understanding of the magnitudes of the related issues.
Participants
The assessment is restricted to a group of environmental health researchers. See participant list in Farmed salmon (project).
Definition
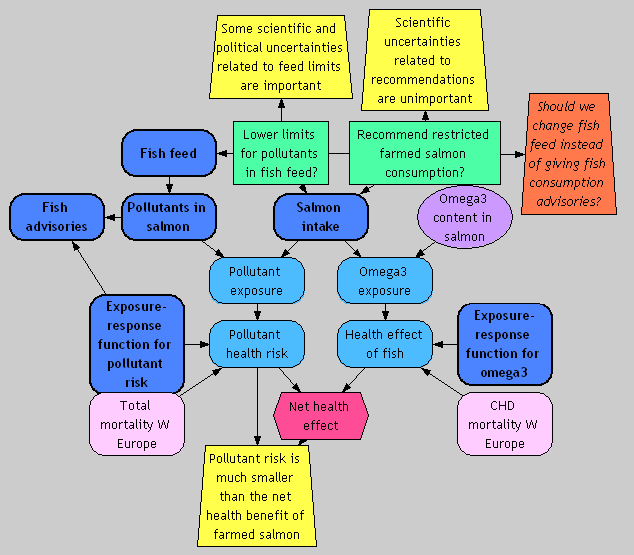
Analyses
- Value of information analyses
- Outcome: Net health effect; Decision: Recommend restricted farmed salmon consumption?; Variables tested: all
- Outcome: Net health effect; Decision: Lower limits for pollutants in fish feed?; Variables tested: all
- Importance analyses
- Outcome: Mortality by recommendation; Variables tested: all
- Outcome: Mortality by feed regulation; Variables tested: all
Result
Results
The main results and conclusions have been published by Tuomisto et al.[2]
Figure. Benefits and risks (number of avoided deaths per year) of eating farmed salmon in Western Europe.
Table: Net health impacts (avoided deaths per year) of eating farmed salmon in Western Europe. The results include the health impacts of the total health impact of omega-3 intake from salmon.
| Statistics or fractile | Business as usual | Recommend restrictions | Stricker rules for feed | Both |
| Mean | 31062 | 22929 | 31428 | 23296 |
| SD | 22650 | 17105 | 22842 | 17317 |
| 0.01 | 576 | 404 | 653 | 460 |
| 0.025 | 1782 | 1286 | 1847 | 1356 |
| 0.05 | 3632 | 2697 | 3766 | 2803 |
| 0.25 | 14547 | 10590 | 14780 | 10793 |
| 0.5 (Median) | 25187 | 18504 | 25479 | 18829 |
| 0.75 | 43064 | 31526 | 43628 | 32091 |
| 0.95 | 76141 | 56697 | 77010 | 57393 |
| 0.975 | 88267 | 66397 | 89040 | 67249 |
| 0.99 | 101832 | 79328 | 102202 | 80143 |
Table: Net health impacts (avoided deaths per year) of eating farmed salmon in Western Europe, compared with the business-as-usual scenario. The results include the health impacts of the total health impact of omega-3 intake from salmon.
| Statistics or fractile | Business as usual | Recommend restrictions | Stricter rules for feed | Both |
| Mean | 0 | -8133 | 366 | -7766 |
| SD | 0 | 9703 | 982 | 9637 |
| 0.01 | 0 | -45895 | -2335 | -45557 |
| 0.025 | 0 | -35624 | -1662 | -35171 |
| 0.05 | 0 | -27745 | -1155 | -27041 |
| 0.25 | 0 | -10929 | -60 | -10553 |
| 0.5 (Median) | 0 | -4876 | 264 | -4560 |
| 0.75 | 0 | -1567 | 820 | -1307 |
| 0.95 | 0 | -112 | 2117 | 147 |
| 0.975 | 0 | -10 | 2635 | 459 |
| 0.99 | 0 | 14 | 3180 | 995 |
Figure. Value of information (VOI) calculated as avoided deaths per year in Western Europe. The first two bars are for the decision about recommending restrictions to salmon consumption. No single variable was important enough to gain any VOI; therefore, only the uncertain variable emphasized by Hites[1] is shown. The other bars are for the decision about setting stricter limits for fish feed.
Conclusions
- Pollutant risk is much smaller than the net health benefit of farmed salmon
- Scientific uncertainties related to recommendations are unimportant
- Some scientific and political uncertainties related to feed limits are important
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 R. A. Hites et al. Global assessment of organic contaminants in farmed salmon. Science, 9 Jan. 2004, p. 226
- ↑ Tuomisto JT, Tuomisto J, Tainio M, Niittynen M, Verkasalo P, Vartiainen T, Kiviranta H, Pekkanen J. Risk-benefit analysis of eating farmed salmon. Science. 2004 Jul 23;305(5683):476-7 Read the article