Plantlibra
 Homepage of the PlantLibra conference
Homepage of the PlantLibra conference
This page is a encyclopedia article.
The page identifier is Op_en3954 |
|---|
| Moderator:Jouni (see all) |
|
|
| Upload data
|
Plantlibra is an EU-funded research project about risks and benefits of plant food supplements.
Plant-based food supplements (PFS) have been and are increasingly used across the European Union, with ingredients often deriving from Third Countries. The knowledge on the safety and benefits of these products – particularly in Europe - is lagging behind the demands of the market and of regulators. Competent authorities, food chain operators and consumers often face difficulties in making informed decisions.
PlantLIBRA aims to foster safe use of food supplements containing or consisting of plants and/or herbal extracts, chiefly by increasing science-based decision-making by regulators and food chain operators, through data, information and tools. PlantLIBRA is structured to develop, validate and disseminate methodologies for risk and benefit assessment, to greatly expand, generate and make available knowledge on PFS, and implement sustainable international cooperation. Through the multi- disciplinary consortium of PlantLIBRA, researchers, excelling in different fields, will share their work and expertise among themselves and with the leading stakeholders towards an integrated "science of botanicals".
- Acronym: PlantLIBRA
- Project ID: 245199
- Call: FP7-KBBE-2009-3
- Programme: FP7
- Activity codes: KBBE-2009-2-4-02
Ideas for consumer perception study
- Question
- What could be asked in the consumer perception study about the benefit-risk assessment?
- Rationale
- A benefit-risk assessment should be useful for some practical purpose. There are two possible uses: the authority uses it to make decisions about acceptability of health claims or products in the market; and the consumer uses it to make informed purchasing decisions. In this study we could and should test for how the consumer perceives the benefit-risk information depending on a) the outcome (i.e. clear vs unclear benefit) and b) way of expressing the conclusion.
- Answer
- The following table describes different pieces of user information that are used to inform the user about the net health benefits of a mock-up PFS product.
| Different ways of expressing outcomes | Different assessment outcomes | |
|---|---|---|
| Net benefit is high | Net benefit is zero | |
| DALY estimates with uncertainties | According to a benefit-risk assessment, using this product for a year will bring more health worth 3 healthy days (uncertainty from 0 to 10 days). | According to a benefit-risk assessment, using this product for a year will bring more health worth 0.5 healthy days (uncertainty from –5 to 6 days). |
| Descriptive without uncertainty | According to a benefit-risk assessment, using this product will bring a small health benefit. | According to a benefit-risk assessment, using this product will bring a negligible health benefit. |
| Descriptive with uncertainty | According to a benefit-risk assessment, using this product will bring a small health benefit (result is uncertain and may be missing). | According to a benefit-risk assessment, using this product is as likely to produce a small health benefit as a small health harm. |
Datbase fields
Composition data
- Bibliographic Reference
Author Title Journal Volume Year Pages Publisher Reference information
- Plant Food Supplement
Plant Food Supplement
- Food Information
Maturity Country of origin Region Season Morphological description Molecular identification Growing condition EuroFIR classification Generic food name Commercial food name GMO Diseased plant Plant description
- Processing
Shape, state or form Heat treatment Cooking method Treatment applied Preservation method
- Sampling Information
Sample year Primary sample unit size Primary sample units Analytical sample size Analytical portion size Analytical portions Portion replicates Sample plan Sample handling
- Compositional Information
Compound class Analytical std.source Analytical method name Analytical method Minimum level Maximum level Standard deviation Mean standard error Aim of the method Purpose of the method Extraction and preparation Identification Activity Compositional comments
- Quality Assessment
Plant/Food description Processing defined Sampling plan Sample handling Compound identification Analytical method Analytical performance Quality code Quality comments
Beneficial data
- Bibliographic Reference
Author Title Journal Volume Year Pages Publisher Reference information
- Plant Food Supplement
Plant Food Supplement
- Food Information
Part Country of origin EuroFIR classification Processed food name Plant remarks
- Processing
Shape, state or form Heat treatment Cooking method Treatment applied Preservation method Processing remarks
- Test Material
Compound class Source Purity Measured quantity Compound remarks
in vitro
Cell type/line Positive control Negative control
in vivo
Route of administration Species Strain/race Gender General population Study subjects Experimental design Concentration/level Control group Clinical aspects Treatment duration Other treatment
in vitro
Standard assay
in vivo
Experiment duration
in vitro
Study remarks
in vivo
Major parameters Gender specific effect
- Results
Result remarks Non-effective level Adverse effects studied Adverse effects, text ADI NOAEL
- Quality Assessment
Study design Subject Test material Conduction of study Methodology Results Quality code Quality comments
- Overall remarks
Overall remarks
Adverse effect data
- Bibliographic Reference
Author Title Journal Volume Year Pages Publisher Reference information
- Plant Food Supplement
Additional information Other bioactive compounds
- Event history
Administration Gender Subject characterization Description of the event
- Adverse effects
Clinical aspects Dose ingested Intake duration Treatment of AE De-challenge / Re-challenge Gender specific effect Conclusion Effective dose Reviewer comments
- Quality Assessment
PFS information Intake Patient history Concurrent diseases Concomitant medications Adverse event Herbal preparation Quality code Quality comments
PFS data
- Identification
Name Trade name Data completed
- Ingredients
Ingredients
- Plant Food Supplement
Interactions Legislation Reference information Links
Important project pages
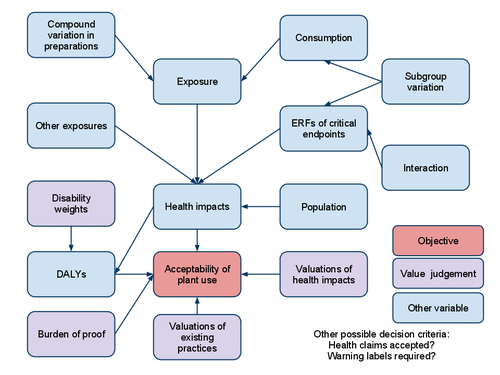
- Compound intake estimator
- Plantlibra deliverable DWP5-6
- Common currency in health assessments
- Valuations of health impacts caused by PFS
- Benefit-risk assessment of food supplements
- Benefit-risk assessment of plant-based food supplements
- Benefit-risk assessment of cinnamon
- Meta-database of biologically active compounds
- File:Benefit-risk assessment for food.ppt
- Cinnamomun verum
Password-protected pages
- heande:Plantlibra
- heande:Composition of bitter fennel essential oil (to Opasnet)
- heande:Composition of plant-based food supplements (to Opasnet)
- heande:Composition of cinnamon dried bark essential oil (to Opasnet)
- heande:Report on methods to estimate intake
- heande:Report on risk-benefit methodologies and on identification of common currency
- heande:Consumption of PFS
- heande:Compound variation in PFS preparations
- heande:Population in PFS assessment
- heande:ERFs of PFS on critical endpoints
- heande:Interaction of PFS with other factors
- heande:Population subgroup variation in respect to PFS
- heande:Burden of proof related to PFS
- heande:Valuations of health impacts caused by PFS
- heande:Valuations of health impacts of PFS, previous assessments
- heande:Valuations of existing practices related to PFS
See also
- Task list for Plantlibra
- Category:Plantlibra
- Category:Plantlibra in Heande
- Proposal for the third project meeting 18th - 21st in Helsinki
- Progress in tasks 5.2, 5.3, 5.4
- eBASIS database
Related files
<mfanonymousfilelist></mfanonymousfilelist>