Benefit-risk assessment of Baltic herring and salmon intake
| [show] |
|---|
Scope
This assessment is part of the WP5 work in Goherr project. Purpose is to evaluate health benefits and risks caused of eating Baltic herring and salmon in four Baltic sea countries (Denmark, Estonia, Finland and Sweden). This assessment is currently on-going.
Question
What are the current population level health benefits and risks of eating Baltic herring and salmon in Finland, Estonia, Denmark and Sweden? How would the health effects change in the future, if consumption of Baltic herring and salmon changes due to actions caused by different management scenarios of Baltic sea fish stocks?
Intended use and users
Results of this assessment are used to inform policy makers about the health impacts of fish. Further, this assessment will be combined with the results of the other Goherr WPs to produce estimates of future health impacts of Baltic fish related to different policy options. Especially, results of this assessment will be used as input in the decision support model built in Goherr WP6.
Participants
- National institute for health and welfare (THL)
- Goherr project group
Boundaries
- Four baltic sea countries (Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Sweden)
- Current situation (fish use year 2016, pollutant levels in fish year 2010?)
- Estimation for future (year 2020?)
Decisions and scenarios
Management scenarios developed in Goherr WP3 frames the following boundaries to the use and consumption of Baltic herring and salmon as human food. Effect of these scenarios to the dioxin levels and the human food use will be evalauted quantitatively and feed into the health benefit-risk model to assess the health effect changes.
- Scenario 1: “Transformation to sustainability”
- Hazardous substances, including dioxins, are gradually flushed out and the dioxin levels in Baltic herring are below or close to the maximum allowable level.
- Fish stocks are allowed to recover to levels, which makes maximum sustainable yield possible and increases the total catches of wild caught fish. The catches of salmon by commercial fisheries has stabilized at low level, while the share of recreational catch increases slightly.
- The use of the Baltic herring catch for food increases. A regional proactive management plan for the use of catch has increased the capacity of the fishing fleets to fish herring for food and through product development and joint marketing, have increased consumer demand for Baltic herring.
- Scenario 2: “Business-as-usual”
- The commercial catches of salmon continue to decrease. The demand for top predatory species, such as salmon and cod remains high, while the demand for herring decreased further as a result of demographic changes.
- Most of the herring catch are used for fish meal and oil production in the region.
- The use of Baltic herring from the southern parts of the Baltic Sea where the dioxin contents are not likely to exceed the maximum allowable level, are prioritised for human consumption. In the absence of the demand in many of the Baltic Sea countries, majority of the herring intended for direct human consumption are exported to Russia.
- Scenario 3: “Inequality”
- The nutrient and dioxins levels continue to decrease slowly.
- The commercial catches of salmon have decreased further as the general attitudes favour recreational fishing, which has also resulted in decreased demand.
- The herring catches have increased slightly, but the availability of herring suitable for human consumption remains low due to both, dioxin levels that remain above the maximum allowable limit in the northern Baltic Sea and the poor capacity to fish for food.
- The use of the catch varies between countries. In Estonia, for example, where the whole catch has been traditionally used for human consumption, there is no significant change in this respect, but in Finland, Sweden and Denmark, herring fishing is predominantly feed directed.
- Scenario 4: “Transformation to protectionism”
- The level of hazardous substances also increases as emission sources are not adequately addressed.
- Commercial salmon fisheries disappears almost completely from the Baltic Sea, although restocking keeps small scale fisheries going.
- Many of the Baltic herring stocks are also fished above the maximum sustainable yield and total catches are declining.
- Owing to the growing dioxin levels detected in herring, majority of the catch is used for aquaculture.
Timing
- Model development during 2016 and 2017
- First set of results in March 2017, draft publication in March 2018
Answer
This section will be updated as soon as preliminary results are available
Results
Conclusions
Rationale
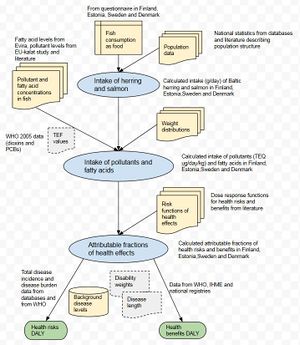
Stakeholders
- Policy makers
- Food safety authorities
- Fisheries management
- Researchers
- Food safety
- Health
- NGO's
- WWF
- Active consumers
- Marine Stewardship Council
- Baltic sea fishers and producers?
Dependencies
Content of all variable pages below are preliminary and will be updated when this assessment proceeds.
- Toxic equivalency factor (TEF)
- Consumption of fish
- Pollutant and fatty acid levels
- Persistent organic pollutant levels in Baltic herring
- Persistent organic pollutant levels in Baltic salmon
- Nutrient levels in fish ----#: . Includes three tables, content modelled with Analytica years ago. How to update these? --Arja (talk) 07:20, 20 October 2016 (UTC) (type: truth; paradigms: science: comment)
- Risk functions of health effects
- Background health data (incidences and DALY)
- Disability weights of health effects
- Length of disease
Analyses
Indices
- Country (Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Sweden)
- Year (current, future)
- Sex
- Age (categories?)
- Fish species (Baltic herring, Baltic salmon)
- Health end-point (ICD-10 code?, name? something else? ----#: . This need to be matched for disability weight, duration of disease, background incidence and disease burden data, dose-responses --Arja (talk) 09:39, 22 September 2016 (UTC) (type: truth; paradigms: science: comment)
- Compound (pollutant, fatty acid) ----#: . This needs to be matched with dose-responses --Arja (talk) 09:39, 22 September 2016 (UTC) (type: truth; paradigms: science: comment)
Calculations
This section will have the actual health benefit-risk model (schematically described in the above figure) written with R. The code will utilise all variables listed in the above Dependencies section. Model results are presented as tables and figures when those are available.
Bayes model for intake
- Model run 28.2.2017 [1]
- Model run 28.2.2017 with corrected survey model [2]
- Model run 28.2.2017 with Mu estimates [3]
- Model run 1.3.2017 [4]
Exposure model
Health impact model (Monte Carlo)
- Model run 13.3.2017: a simple copy of op_fi:Silakan hyöty-riskiarvio [5]
- Model run 13.3.2017 with showLocations function [6]
Plot concentrations and survey
- Requires codes Op_en7748/bayes and indirectly Op_en7748/preprocess.
- Model run 1.3.2017 [7]
References
Keywords
See also
- Risk and Benefit Assessment of Herring and Salmonid Fish from the Baltic Sea Area
- Swedish Market Basket 2010
- Riksmaten 2010
- Danskernes kostvaner 2011-2013


