Helsinki energy decision 2015: Difference between revisions
m (→See also) |
m (→See also) |
||
| Line 308: | Line 308: | ||
{{Helsinki energy decision 2015}} | {{Helsinki energy decision 2015}} | ||
* [http://www.ymparisto.fi/helenbioYVA Helsingin Energian biopolttoaineiden käytön lisääminen, Helsinki] | * [http://www.ymparisto.fi/helenbioYVA Helsingin Energian biopolttoaineiden käytön lisääminen, Helsinki YVA 2013] | ||
* [[OpasnetUtils/Drafts]] | * [[OpasnetUtils/Drafts]] | ||
* [[Population of Finland]] | * [[Population of Finland]] | ||
Revision as of 06:47, 18 June 2015
| [show] |
|---|
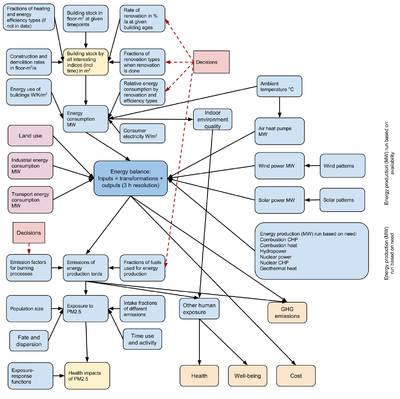
Scope
Question
What options does Helsinki have for main energy solutions, and which options are good or bad in terms of
- climate mitigation,
- stability (fuel availability etc),
- cost to the city and citizens,
- environment,
- biofuel use,
- national energy balance,
- domestic source,
- health?[1]
Intended use and users
Helsinki City Council will make a major decision in autumn 2015 about renovating old power plants, building a new one, or some other option replacing the need of the old power plants. Therefore, the City Council is the major user of the assessment. There are also secondary uses, such as informing national energy discussion and demonstrating the usefulness of an open combined energy balance and building model.
Participants
The work is coordinated by Jouni Tuomisto from THL / Impact Assessment Unit. Their motivation is to assess the environmental health aspects of the decision. Participants that we hope get involved when they are informed about the assessment include (not in any particular order)
- THL: Jouni, Pauli, Teemu, Matleena, Julia, Olli
- the City of Helsinki,
- Helen energy company,
- Jorma Jokiniemi (expert in emission factors from UEF),
- Osmo Soininvaara (politician, economist from Helsinki),
- Peter Lund (energy expert from Aalto University),
- Niko Karvosenoja (air emission expert from SYKE),
- Sanna Syri (energy expert from SYKE),
- Sanni Väisänen (expert in greenhouse gas emission factors).
- Matti Jantunen (expert in environmental health, exposure, and energy)
- Satu Taavitsainen, parliamentarist, chairman of Mikkeli city council [2]
- Maria Kopsakangas-Savolainen (energy costs and pricing, SYKE [3])
Boundaries
- Time: 2015 - 2060
- Energy need estimated for Helsinki.
- Main focus is on local heat and power need. Energy balance estimated for Helsinki (electricity nationally).
- Health impacts estimated for the regional area (ca. 300 km radius)
- Impacts are assessed separately for the citizen, the city, Helen energy company, and Finland.
- Transport is not looked at although it is an important energy consumer. This is because there is no interaction with heating except via city structure, and there are no resources to look at that in this assessment. Electric cars would have an interaction with electricity production, but that applies to the total electricity market area (Finland, partly Scandinavia) and is too complex to look at.
Decisions and scenarios
- Main article: Helsinki energy decision options 2015
The two options in the official decision preparation are Hanasaari shutdown and Vuosaari, and Hanasaari 40 bio and Salmisaari 40 bio. However, also other options have been suggested, and also they are evaluated at least superficially.
- BAU: Only small, essential renovations are made to current power plants to stay within new emission limits.
- Vuosaari: A new power plant is built in Vuosaari with the capacity to burn 100 % wood-based fuel or any combination of wood-based fuels and coal.
- Hanasaari shutdown: The Hanasaari powerplant is shut down, demolished and apartment buildings are built in its place.
- Hanasaari 40 bio: The Hanasaari power plant is renovated to burn 40% wood-based fuels and 60% coal.
- Salmisaari 40 bio: The Salmisaari power plants are renovated to burn 40% wood-based fuels and 60% coal.
- Biofueled heat production units: Salmisaari oilfueled heat plant is shut down and new biofuel burning heat plants are built in Salmisaari and Vuorsaari.
- Loviisa nuclear CHP: A third nuclear power plant is built in Loviisa and the heat is used for district heating in Helsinki.
- Neste excess heat: The excess heat from the Neste's oil refinery in Porvoo is used for district heating in Helsinki.
- Decentralised energy production: The amount of decentralised energy production is increased as much as possible. Practically this means building a lot more solar panels, geothermal power, small-scale wood burning and wind mills around Helsinki.
- Large heat pumps: Big heat pumps are installed to draw heat from the Baltic sea or deep from the ground to produce district heating.
- Energy saving: With huge energy saving campaigns and by renovating buildings to be more energy efficient the amount of required energy is decreased significantly.
Timing
The assessment started in May 2015. First draft results are expected before midsummer 2015. Final results should be available well before the City Council makes the decision in autumn, which means that results should exist by September 15th, 2015.
Answer
Results
Conclusions
Rationale
Politics is not about getting your mind. It is about learning about good and bad actions based on values. Negotiations are useful only when you know which actions promote your values.
Costs of fuel. Costs on energy type in general. Predict fuel prices into the future and adjust. How do you minimize a matrix? Run lots of iterations and select from oosterior distribution?
Stakeholders
The impacts are assessed and valued from the point of view of the following stakeholders:
- The city of Helsinki
- Helen Oy energy company
- A citizen of Helsinki
- Finland
- Global view
Dependencies
List of pages used in model:
- Helsinki energy decision 2015
- Helsinki energy decision options 2015
- Climate change policies in Helsinki
- Climate change policies and health in Kuopio
- Burden of disease in Finland
- Exposure-response function
- ERFs of environmental pollutants
- ERF of several environmental pollutions
- ERF of omega-3 fatty acids
- ERF of methylmercury
- ERF of dioxin
- Exposures in Finland
- Health impact assessment
- Disease risk
- Population attributable fraction
- Population of Helsinki metropolitan area
- Intake fractions of PM
- Exposure to PM2.5 in Finland
- Building model
- Building stock in Helsinki
- Energy use of buildings
- Energy balance in Helsinki
- Energy balance in Kuopio
- Energy balance
- Helsinki energy production
- Emission factors for burning processes
- Emission assessment of small-scale energy production in the Helsinki metropolitan area
- OpasnetUtils/Drafts
Other data that we need to check where it goes.
- Soininvaara 2010: Helsingin lämmitys
 Assessment of small-scale energy production in Helsinki Metropolitan area
Assessment of small-scale energy production in Helsinki Metropolitan area- Helsingin Energian biopolttoaineiden käytön lisääminen, Helsinki YVA 2013
- Tekniikka ja talous 2015: Yllätyskortti Helsingin energiapelissä.
- Helsingin rakennusvalvonnan ohjeet
| [show]Variable | Measure | Indices |
|---|
Analyses
- Cost-benefit analysis of different options. Costs considered: capital and operational costs of energy production, climate costs (CO2e emissions converted to euros), health (DALYs converted to euros).
- Total capacity availability and feasibility (applies especially to decentralised option).
- Temporal heat and power demand and supply (hourly resolution).
Indices
- Temporal: Month (non-marginal), Hour (non-marginal), Year (2015, 2025, 2040, 2060)
- Temperature (Very cold (< -20 C), Cold (-20- -5 C), Cool (-5 - 5 C), Mild (5 - 14 C), Warm (15 - 23 C; neither heating nor cooling need in residences), Hot (> 24 C; cooling need)
- Decisions (options 1-7)
- Stakeholder (Citizen, City, Helen, Finland)
- Spatial: City area (summed up after energy need)
- Health: Disease (any disease that is linked to Exposure agents emitted)
- Emission, exposure: Exposure agent (any agent that is emitted by energy production)
- Energy production: Burner, Fuel, Heating.
- Buildings: Building [use type], Heating, Constructed, City area, Renovation, Efficiency.
Calculations
See also
- Helsingin Energian biopolttoaineiden käytön lisääminen, Helsinki YVA 2013
- OpasnetUtils/Drafts
- Population of Finland
- Climate change policies and health in Kuopio DALY weights etc
- Helsinki's two options
- Halme et al. 2014 Kasvua ja työllisyyttä uudella energiapolitiikalla
- Domestic energy use map of Britain [http://www.undertheraedar.com/2011/09/energy-consumption-in-london.html Energy consumption in London [5]
- Energiatodistusrekisteri (Helsingistä yli 300 rakennusta)
- Building energy use in New York City
Things to memorize
Units needed:
- Work, energy, työ: joule J = Nm. 1 J = work needed to move an object by 1 m using a force of 1 N.
- 1 kWh kilowatt-hour = 1000 W * 1 hour = 1000 W * 3600 s = 3.6 MJ
- Force, voima: Newton N. E.g. the gravity force of 1 kg object is 9.8 N
- Power, teho: J/s = W (watt) Note that power also means electricity.
Useful pieces of data.
- To heat 1 kg of water from 0 to 100 C takes 420 kJ = 0.42 MJ = 0.12 kWh.
- To boil 1 kg of water to vapor takes 2300 kJ = 2.3 MJ
- Coal contains ca. 40 MJ/kg
- Wood contains ca. 17 MJ/kg
- Wood chips contain ca 7 MJ/kg (because of moisture)
- Fine particles kill 1800 people/a in Finland.
- When you burn 1 kg of coal, you get 3.7 kg of CO2.
- A typical industial-size wind mill produces max 3 MW of electricity
- A large power-plant produces 200-1500 MW of electricity.
Prefixes:
- µ micro 10-6 0.000001
- m milli 10-3 0.001
- 1
- k kilo 103 1000
- M mega 106 1000000
- G giga 109 1000000000
- T tera 1012 1000000000000
- P peta 1015 1000000000000000
Keywords
Energy, renewable energy, nuclear energy, fossil energy, wood pellets, power plants, district heating, decentralised energy production, centralised energy production, cost-effectiveness
References
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 1.2 Halme, Minna; Hukkinen, Janne; Korppi-Tommola, Jouko; Linnanen, Lassi; Liski, Matti; Lovio, Raimo; Lund, Peter; Luukkanen, Jyrki; Nokso-Koivisto, Oskari; Partanen, Jarmo; Wilenius, Markku. Kasvua ja työllisyyttä uudella energiapolitiikalla. Jyväskylän yliopiston julkaisuja 2014. [1]
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedjudl - ↑ Sanni Väisänen: Greenhouse gas emissions from peat and biomass-derived fuels, electricity and heat — Estimation of various production chains by using LCA methodology
Related files
 Assessment of small-scale energy production in Helsinki Metropolitan area ←--#: . This contains all Pasi's assessment's data tables and is very useful! --Jouni (talk) 17:05, 14 May 2015 (UTC) (type: truth; paradigms: science: defence)
Assessment of small-scale energy production in Helsinki Metropolitan area ←--#: . This contains all Pasi's assessment's data tables and is very useful! --Jouni (talk) 17:05, 14 May 2015 (UTC) (type: truth; paradigms: science: defence)