Helsinki energy decision options 2015
BAU
In Business as usual -option coal remains the main fuel in Hanasaari B and Salmisaari B power plants, but the use of biofuels is increased to 5−10 % and the changes to power plants required in the new Industrial Emission Directive (IED) are made. These changes have already been approved and some are already done, so they will happen no matter what is decided about the rest of the options.
The IED sets new emission limit values (ELVs) to power plants within the European Union, which will be in effect as of 1.1.2016. In order to stay within the new ELVs, both Hanasaari and Salmisaari power plants must be renovated.[1]
The changes to be made in Hanasaari are:[1]
- Enhancing sulphur removal
- Selective catalytic reduction (SCR) or selective non-catalytic reduction (SNCR), or polttotekniset ratkaisut (combustion-technical solutions???)
- Renewing the electric filters or enhancing their operation
The changes to be made in Salmisaari are:[1]
- Enhancing sulphur removal
- Selective catalytic reduction (SCR) or selective non-catalytic reduction (SNCR), or polttotekniset ratkaisut (combustion-technical solutions???)
- Renewing the electric filters or enhancing their operation
Emissions
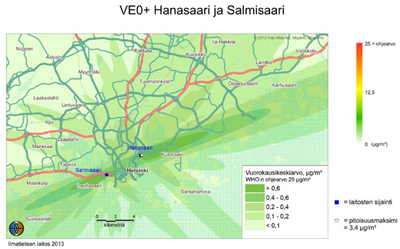
Hanasaari receives a maximum of 11 pellet deliveries per day and Salmisaari max 14/d.[1]
| Option | Fly ash (t/a) | Bottom ash (t/a) | Sulphur-removal end product (t/a) | Total (t/a) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hanasaari power plant: biofuels 10 % | 59 000 | 12 000 | 8 000 | 79 000 |
| Salmisaari power plant: biofiels 10 % | 45 000 | 11 000 | 9 000 | 65 000 |
| Total | 104 000 | 23 000 | 17 000 | 144 000 |
| Emission source | CO2 kt/a | CO2-eqv kt/a (incl. fossil fuel ghg-emissions) | CO2-eqv kt/a (incl. fossil and biofuel emissions) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power plant emissions | 2 524 | 2 533 | 2 687 |
| Emissions from fuel transport | 8 | ||
| Total | 2 540 | 2 700 |
| Power plant | NO2 (t/a) | SO2 (t/a) | Particles (t/a) |
| Salmisaari A and B | 946 | 996 | 92 |
| Fly ash (t) | Bottom ash (t) | Sulphur removal end product (t) | Total (t) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salmisaari power plants: 10 % bio, 90 % coal | 45 000 | 11 000 | 9 000 | 65 000 |
Emission coefficients
Cost
No building cost, because nothing is renovated nor built.
Usage cost
Production
How much energy?
| Electricity MW | Heat MW | Fuel | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hanasaari | 220 | 420 | coal, pellets |
| Salmisaari | 160 | 300 | coal, pellets |
| Total | 380 | 720 |
Same table as in VE2(?), because same power plants will be in use.
Vuosaari
A new power plant is built in Vuosaari. The new plant (Vuosaari C) can burn any ratio of biofuel to coal. An energy tunnel is built from Vuosaari to Hanasaari to transport the energy to Helsinki city center.
Effects:
- Emissions
- Cost
- Traffic
- Noise (Natura 2000 -area nearby)
- Air quality
- Forests close by and further away in Finland
- Drawing closer to the coal-neutrality goal
- Running level
- Jobs in construction
- Decision-maker: Helsinki city, Helen
Description
The plans for power plant Vuosaari C are based on the assumption, that the plant will mostly use biofuels (max 80%) and coal (20%). The planned fuels are wood chips and pellets as well as small amounts of agro-biomass. The use of biochar is also possible.[1] The plan is to get 60 % of the biofuel from Finland.[2]
The plant will be fitted with a boiler developed for biofuel combustion (specifically kiertoleijupetikattila ). In order to ensure stable levels of district heat the plant is planned so, that it can function using coal only. Nevertheless plans can be made to enable the use 100 % biofuels. The recent Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) compared the options of burning 100 % biofuels with the extreme option of burning 100 5 coal.[1]
Three options are considered for the Vuosaari powerplant (in this option, Salmisaari always burns 95% coal and 5% biofuels):
- V1: 80% biofuels, 20% coal
- V2: 100% biomass
- V3: 100% coal
At the same time Helsinki is planning a 12 kilometres long energy tunnel from Vuosaari to Hanasaari. It would be quarried in bedrock and provide district heating and possibly electricity for the needs of the whole city. The warehouses for fuel, locations for unloading trains and trucks and conveyor would be built next to the plant, and possibly a road for crossing the train tracks as well.[1]
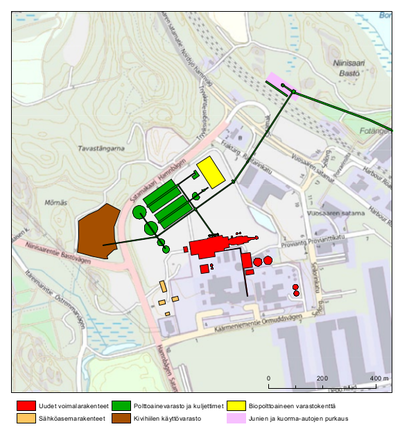
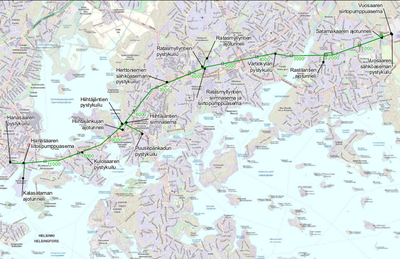
Emissions
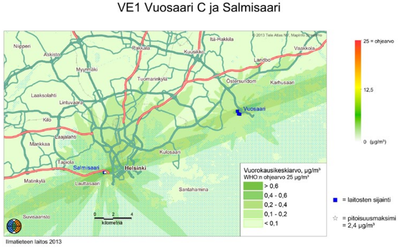
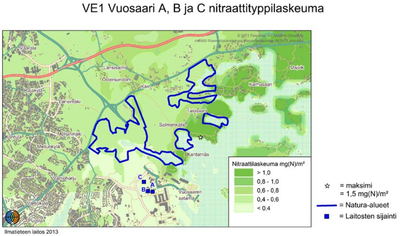
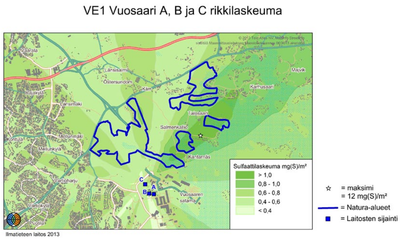
The emissions from the new plant would have two main sources: combustion of biofuels and coal and from transporting those fuels to Vuosaari C.
The fuel will be brought to the plant by ship, barge, train and truck. Ships and barges will be used to transport biofuel, coal and oil. Trains and trucks will mainly be used for transporting biofuels, trains also for transporting coal. Because the amounts of fuel required by the C-plant will be substantial, the fuel shipments will mostly be carried out using ships. Trains and trucks will be a supplementary means of transport. Shipments can be brought 24/7.[1]
Flue gases will be conducted to flue gas purification, where the particles are remowed, after which the flue gases are directed through flue gas blowers into the chimney. The ashes from the fuel are remowed as bottom ash from the furnace and as fly ash in the flue gas purification.
The power plant's flue gases are purified efficiently, so harmful effects to nearby vegetation remain slight. The great height of the chimney aids in the effective dilution of emissions in the air, so the effects on local concentrations are minimized. Judging by the atmospheric fate and transport (AFT) modeling's calculations, the new power plant C would cause only a minimal increase in air impurity levels in the metropolitan area. It is estimated that the fallout wont have harmful impacts on the vegetation of Natura-areas in Östersundom bird waters and Mustavuori grove nor further away north-east in Sipoonkorpi's Natura-area.[1]
Judging by the AFT-modeling's results, the nitrogen oxide-, sulfur oxide- or particulate matter emissions from the normal operation of Helsingin Energia's powerplants do not cause a health risk to the residents in the neighbouring area. In each Vuosaari option the plants' emission levels are lower than the recommended values and limit values for air quality, which have been decreed in order to protect health. In evaluating the results of the AFT-modeling it needs to be considered, that the enviromental impact assessment (EIA) did not review the plants' possible emissions in a fault situation or the combined impact on air quality of the plants and other sources of emissions in te area.[1]
| Power plant | NO2 (t/a) | SO2 (t/a) | Particles (t/a) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vuosaari C | 853 | 853 | 57 |
| Vuosaari A and B | 550 | - | - |
| Total | 2 349 | 1 849 | 149 |
| Sub-option | Fly ash (t) | Bottom ash (t) | Sulphur removal end product (t) | Total (t) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V1 80 % bio, 20 % coal | 59 000 | 10 000 | - | 69 000 |
| V2 100 % bio (10 % pellet, 90 % chips) | 52 000 | 9 800 | - | 62 000 |
| V3 100 % coal | 82 000 | 52 000 | - | 134 000 |
| CO2, kt/a | CO2-ekv, kt/a (incl. fossilfuel ghg emissions) | CO2-ekv, kt/a (incl. fossilfuel and biofuel emissions) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| V1 powerplant emissions | 1 468 | 1 402 | 3 061 |
| V2 powerplant emissions | 1 073 | 1 114 | 3 090 |
| V3 powerplant emissions | 2 722 | 2 882 | 2 947 |
| V1 fuel transport emissions | 15 | ||
| V2 fuel transport emissions | 23 | ||
| V3 fuel transport emissions | 6 | ||
| V1 total emissions | 1 480 | 3 080 | |
| V2 total emissions | 1 140 | 3 110 | |
| V3 total emissions | 2 890 | 2 950 |
Cost
Building cost
The recent Environmental Impact Assessment takes a quick look at the different energy investment options' economic effects. A project plan will made later in 2015 and give more precise details on the economic effects. Building the new power plant would probably be twice as expensive as making the necessary changes in the old plants. Assessing the economic effects is not simple, however. Using the Vuosaari C plant would be tens of millions cheaper yearly than using the overhauled Hanasaari and Salmisaari plants. The city of Helsinki will lose money also if they can not build a new residential area in Hanasaari as planned.[2]Helsingin Sanomat: Helsingin vaihtoehdot: Kallis voimala luonnonsuojelualueen viereen tai Hanasaari ilman asuntoja</ref>
The power plant itself will cost approximately 650 million euros and the energy tunnel 180 million euros. An estimate (2011) of the total costs is 1,2 billion.[3]
Usage cost
If the Vuosaari C powerplant uses 100 % biofuels (ratio: 90 % wood chips to 10 % pellets), it would mean an annual fuel amount of 1,8 million tons wood chips and 103 000 tons pellets.
If the portion of biofuels is 80 % (ratio: 90 % wood chips to 10 % pellets), it would mean an annual fuel amount of 1,46 million tons wood chips, 82 000 tons pellets and 140 000 tons coal.
If the Vuosaari C powerplant uses coal only, it would need 660 000 tons of it per year.[1]
The export price on wood pellets is 133 €/t [1].
The price of wood chips is 20€/MWh? [2][3]
According to this page, the thermal coal CAPP price is about 50 €/metric tonne.
| Coal | Wood chips | Wood pellet | ||
| Fuel consumption | t/h | 0–108 | 0–334 | 0–178 |
| Fuel consumption | m3/h | 0–135 | 0–1 113 | 0–255 |
Calculations:
If 100% coal is used in Vuosaari power plant
- 660 000 t/a * 50 €/t = 33 000 000 €/a
If only 20% coal was used:
- coal: 140 000 t/a * 50€/t = 7 000 000 €/a
- pellets: 82 000 t/a * 133 €/t = 10 906 000 €/t
- hake: 1 460 000 t/a * €/t =
If only biofuels were used:
- hake: 1 800 000 t/a * €/t =
- pellets: 103 000 t/a * 133 €/t = 13 699 000 €/a
Production
The annual fuel consumption will be approximately 4 TWh depending on the year and the way the plant is run.[1] The new plant's district heat output would be around 350 MW and electricity output 200 MW.[4]
Around 40-50 % of the heat is conducted to the furnaces' walls and the possible superheater. The rest of the heat is transferred in the convection part.[1]
Effects to Natura 2000 area
The wind predominantly blows from south-west. The noise barrier in the harbour and especially the wooded area in Niinisaari limit the spread of emissions towards north-east and e.g. the Natura area. The vegetation binds dust especially in summer time.[1]
Hanasaari shutdown
Hanasaari power plant is shut down and demolished. Apartment buildings are constructed in its place.
Effects:
- Emissions
- Cost
- Land use near city center
- Market rates for apartments in Helsinki
- Quality of inner city environment
- Running level
- Jobs in construction
- Decision-maker: Helsinki city, Helen
Emissions
Cost
Hanasaari 40 biofuel
Hanasaari power plant is renovated to burn 40% biofuels among coal.
Effects:
- Emissions
- Cost
- Forests around Finland
- Running level
- Economy of cities selling biofuels
- Jobs in construction
- Decision-maker: Helsinki city, Helen

Emissions
Pellets are transported to Hanasaari mainly by ship. An estimated 18 truckloads of pellet would come to Hanasaari each day. Approximately 100 ships annually would ship coal and pellets to Hanasaari.[1]
A research paper published in 2014 assessed the net environmental impacts of the co-combustion and changes in urban air quality connected to pellet transport, and aimed to identify environmental hotspots relevant to possible future higher-share co-combustion. The applied methods were screening LCA (life cycle assessment) and fine particle dispersion modelling. Its results were that low-share wood pellet co-combustion in CHP production leads to net environmental impact reductions and does not deteriorate air quality in the urban environment. If higher-share co-combustion were to be implemented, the environmental hotspots to focus on would be the operational issues of a power plant and the origin and sustainability aspects of wood pellet production.[5]
| NO2 (t/a) | SO2 (t/a) | Particles (t/a) | |
| Hanasaari B | 1 224 | 1 224 | 122 |
| Fly ash (t/a) | Bottom ash (t/a) | Sulphur removal end product (t/a) | Total (t/a) | |
| Hanasaari power plant: 40 % biofuels, 60 % coal | 40 000 | 9 000 | 6 000 | 54 000 |
| CO2, kt/a | CO2-eqv, kt/a (incl. fossilfuel ghg-emissions) | CO2-ekv, kt/a (incl. fossilfuel and biofuel emissions) | |
| Power plant emissions | 1 594 | 1 606 | 2 837 |
| Fuel transport emissions | 11 | ||
| Total | 1 620 | 2 850 |
Emission coefficients
Cost
Building cost
The powerplant by itself would cost 100 million euros, the total effect on Helsingin Energia's investment costs would be 500 million (an estimate of 2011).[3]
Usage cost
In the option Hanasaari 40 % biofuel the plabt uses around 390 000 tons coal and 380 000 tons pellet per year. An estimated 11 500 tons of oil per year would be used as support and back-up fuel.[1]
Production
| Electricity MW | Heat MW | Fuel | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hanasaari | 220 | 420 | coal, pellets |
Salmisaari 40 biofuel
Salmisaari power plant is renovated to burn 40% biofuels among coal.
Effects:
- Emissions
- Cost
- Forests around Finland
- Running level
- Economy of cities selling biofuels
- Jobs in construction
- Decision-maker: Helsinki city, Helen
The pellets are transported to Salmisaari power plant by truck. The estimate is, that to burn 40 % biofuels it would need 53 truck shipments of pellets per day. Helsingin Energia is looking into an option, where the pellets to Salmisaari would be brought also through Hanasaari harbour. If all pellets for Salmisaari's use were transported through Hanasaari, the number of ships coming to its harbour transporting coal and pellets would increase by 90 per year.[1]
Emissions
| Power plant unit | NO2 (t/a) | SO2 (t/a) | Particles (t/a) |
| Salmisaari A and B | 946 | 996 | 92 |
| Fly ash (t/a) | Bottom ash (t/a) | Sulphur removal end product (t/a) | Total (t/a) | |
| Salmisaari power plant: 40 % biofuels, 60 % coal | 30 000 | 8 000 | 6 000 | 44 000 |
| CO2, kt/a | CO2-eqv, kt/a (incl. fossilfuel ghg-emissions) | CO2-ekv, kt/a (incl. fossilfuel and biofuel emissions) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power plant emissions | 1 594 | 1 606 | 2 837 |
| Fuel transport emissions | 11 | ||
| Total | 1 620 | 2 850 |
The Salmisaari plant uses around 290 000 tons coal and 280 000 tons pellet per year. Approximately 11 500 tons of oil per year are used as support and back-up fuel.[1]
| Electricity MW | Heat MW | Fuel | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Salmisaari | 160 | 300 | coal, pellets |
Cost
Production
Biofueled heat production units
Salmisaari oilfueled heat plant is shut down and new biofuel burning heat plants are built in Salmisaari and Vuorsaari.
Effects:
- Emissions
- Cost
- Forests around Finland
- Running level
- Economy of cities selling biofuels
- Jobs in construction
- Decision-maker: Helsinki city, Helen
Loviisa nuclear CHP
A new nuclear power plant is built in Loviisa and used for district heating in Helsinki.
Effects:
- Emissions
- Cost
- Nuclear waste
- Perceived safety
- Running level
- Jobs in construction
- Decision-maker: Helsinki city, Fortum, Loviisa city?
Neste excess heat
Excess heat from Neste's oil refinery in Porvoo is used for district heating in Helsinki.
Effects:
- Cost
- Running level
- Jobs in construction
- Decision-maker: Helsinki city, Neste
Decentralised energy production
Small-scale energy production units are built around Helsinki, such as heat pumps, geothermal, sun panels, wood burners and wind mills for producing energy for a single building.
Effects:
- Emissions
- Cost
- Running level
- Tourism & image
- Jobs in construction
- Jobs in research?
- Decision-maker: Helsinki city, Citizens
Large heat pumps
Heat pumps are installed to draw large amounts of heat from the Gulf of Finland (similar system as in Stockholm) or from deep drilled hole from the ground (similar system as piloted in Espoo).
Effects:
- Emissions
- Cost
- Baltic sea
- Running level
- Environmental and political concerns
- Tourism & Finland's imago
- Jobs in construction
- Decision-maker: Helsinki city
Energy saving
Buildings in Helsinki are renovated, big campaigns to affect attitudes are organised and zero-energy houses are built to reduce the consumption of power significantly.
Effects:
- Emissions
- Cost
- Tourism & Finland's imago
- Running level
- Jobs in construction
- Decicion-maker: Helsinki city, Citizens
See also
- Net environmental impacts of low-share wood pellet co-combustion in an existing coal-fired CHP (combined heat and power) production in Helsinki, Finland[5]
- Helsingin parhaat energiatehokkuuskäytännöt -työryhmän loppuraportti 2011
References
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15 1.16 1.17 1.18 1.19 1.20 1.21 1.22 1.23 1.24 1.25 1.26 1.27 1.28 1.29 1.30 1.31 1.32 1.33 1.34 1.35 1.36 1.37 1.38 Helsingin Energian biopolttoaineiden käytön lisääminen, Helsinki YVA 2013
- ↑ Jump up to: 2.0 2.1 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedhs2 - ↑ Jump up to: 3.0 3.1 Helsingin Sanomat: Näistä isoista investoinneista päätetään
- ↑ Helsingin Energia
- ↑ Jump up to: 5.0 5.1 Jáchym Judl, Sirkka Koskela, Timo Korpela, Niko Karvosenoja, Anna Häyrinen, Jari Rantsi. Net environmental impacts of low-share wood pellet co-combustion in an existing coal-fired CHP (combined heat and power) production in Helsinki, Finland. Energy 77 (2014) 844-851. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2014.09.068
- ↑ Helen: Hanasaaren voimala