ERF of omega-3 fatty acids
| Moderator:Olli (see all) |
|
|
| Upload data
|
Scope
What is the exposure-response function (ERF) of omega-3 fatty acids?
Definition
Exposure-response of fish oil intake for MI risk in adults is indexed by variable age. It applies to the last two age categories.
Data
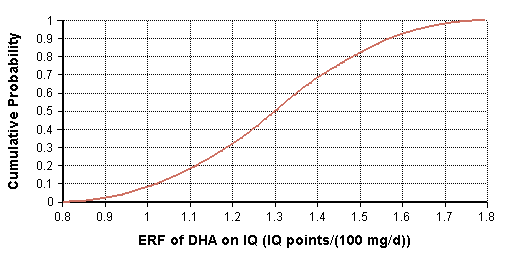
The study by Cohen et al. 2005 [1] estimates that increasing maternal docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) intake by 100 mg/day increases child's IQ by 0.13 points D↷. This value represents central estimate while the upper and lower bound for this ERF is 0.08 and 0.18. Triangular distribution is used.
Dependencies
None defined.
Unit
IQ points/(100mg omega-3/d)
Formula
Result
{{#opasnet_base_link:Op_en5830}}
| Obs | Disease | Response metric | Exposure route | Exposure metric | Exposure unit | Threshold | ERF parameter | ERF | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | IQ change | placenta | IQ points/(100mg omega-3/d) | ||||||
| 2 | myocardial infarction | fish ingestion |
References
- ↑ Cohen, J.T., PhD, Bellinger, D.C, PhD, W.E., MD, Bennett A., and Shaywitz B.A. 2005b. A Quantitative Analysis of Prenatal Intake of n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Cognitive Development. American Journal of Preventive Medicine 2005;29(4):366–374).