Insight network: Difference between revisions
(→Process: link to code) |
(→Calculations: chooseGr function added to server code) |
||
| Line 857: | Line 857: | ||
} | } | ||
objects.store(ui) | |||
cat("Function ui stored (makeUi is depreciated and not stored). Usage: shinyApp(ui, server, enableBookmarking = 'url')\n") | |||
objects.store(ui | |||
cat("Function ui stored (makeUi is | |||
</rcode> | </rcode> | ||
| Line 866: | Line 864: | ||
# This is code Op_en3861/server on page [[Insight diagram]]. | # This is code Op_en3861/server on page [[Insight diagram]]. | ||
library(OpasnetUtils) | library(OpasnetUtils) | ||
#' Function chooseGr takes a diagrammer graph and selects s subgraph based on topic, labels, steps from selected nodes etc. | |||
#' @param gr diagrammer graph | |||
#' @param input list of arguments to be used in selection | |||
#' @seeds ovariable where @data has columns Topic to be chosen and Node for Oldid's to select. | |||
#' @return diagrammer graph where node_selection contains the selected nodes | |||
chooseGr <- function(gr, input, seeds) { | |||
nods <- union(c( | |||
match(seeds@data$Node[seeds@data$Topic==input$topic], gr$nodes_df$Oldid), | |||
match(input$addnodes, gr$nodes_df$label)), | |||
match(input$addnodesByOldid, gr$nodes_df$Oldid) | |||
) | |||
nods <- nods[!is.na(nods)] | |||
gr <- deselect_nodes(gr, get_selection(gr)) | |||
gr <- select_nodes_by_id(gr, nods) | |||
if(input$steps>0) { | |||
for(i in 1:input$steps) { | |||
gr <- deselect_nodes(gr,match(input$removenodes, gr$nodes_df$label)) | |||
gr <- trav_both(gr,add_to_selection = TRUE) | |||
} | |||
if("Remove branches only" %in% input$formatting) { | |||
gr <- select_nodes_by_id(gr,match(input$removenodes, gr$nodes_df$label)) | |||
} else { | |||
gr <- deselect_nodes(gr,match(input$removenodes, gr$nodes_df$label)) | |||
} | |||
} | |||
if("Show legend nodes" %in% input$formatting) { | |||
gr <- select_nodes_by_id(gr, match(seeds@data$Node[seeds@data$Topic=="Selitykset"], gr$nodes_df$Oldid)) | |||
} | |||
gr <- deselect_nodes(gr, match(input$ignoreobj, gr$nodes_df$type)) | |||
return(gr) | |||
} | |||
#### Create shiny server at file server.R | #### Create shiny server at file server.R | ||
server <- function(input, output, session) { | server <- function(input, output, session) { | ||
output$plot1 <- renderGrViz({ | output$plot1 <- renderGrViz({ | ||
gr2 <- chooseGr(gr = gr, input = input, seeds = seeds) | |||
# gr <- deselect_nodes(gr, union( # This should find the INTERCEPT of from is selected AND to is selected and rel %in% ignorerel. | # gr <- deselect_nodes(gr, union( # This should find the INTERCEPT of from is selected AND to is selected and rel %in% ignorerel. | ||
# However, it is more complicated than that, because we may not want both from and to to disappear, only the one who is further away from core. | # However, it is more complicated than that, because we may not want both from and to to disappear, only the one who is further away from core. | ||
| Line 901: | Line 909: | ||
# tmp$edges_df$to[tmp$edges_df$rel %in% input$ignorerel] | # tmp$edges_df$to[tmp$edges_df$rel %in% input$ignorerel] | ||
# )) | # )) | ||
gr2$nodes_df$label <- gsub("(.{1,18})(\\s|$)", "\\1\n", gr2$nodes_df$label) # Cut labels to max 18 characters long on one line (except if a word is longer) | gr2$nodes_df$label <- gsub("(.{1,18})(\\s|$)", "\\1\n", gr2$nodes_df$label) # Cut labels to max 18 characters long on one line (except if a word is longer) | ||
# Alternative possibility is to use strwrap function from {base} or stri_wrap from stringi. | # Alternative possibility is to use strwrap function from {base} or stri_wrap from stringi. | ||
if("Hide node labels" %in% input$formatting) gr2$nodes_df$label <- "" | if("Hide node labels" %in% input$formatting) gr2$nodes_df$label <- "" | ||
if("Hide edge labels" %in% input$formatting) gr2$edges_df$label <- " " | if("Hide edge labels" %in% input$formatting) gr2$edges_df$label <- " " | ||
grViz(generate_dot(transform_to_subgraph_ws(gr2))) | grViz(generate_dot(transform_to_subgraph_ws(gr2))) | ||
}) | }) | ||
| Line 926: | Line 929: | ||
} | } | ||
objects.store(server) | objects.store(chooseGr, server) | ||
cat(" | cat("Functions chooseGr, server stored. Usage: shinyApp(ui, server, enableBookmarking = 'url')\n") | ||
</rcode> | </rcode> | ||
Revision as of 08:08, 21 December 2018
| Moderator:Jouni (see all) |
|
|
| Upload data
|
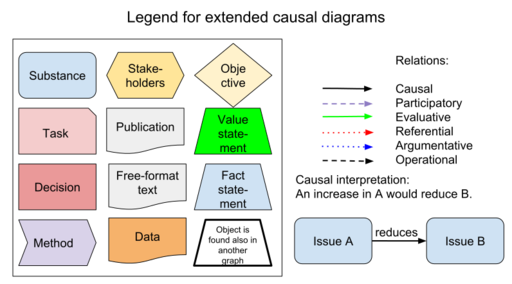
Insight networks are graphical representations of a particular situation, where the objects described are causally related to each other. In addition, the diagrams contain non-causal elements such as value judgements or inferences based on data. Insight networks utilise the ideas of directed acyclic graphs, but they have additional features.
Question
What notation is simple and flexible enough so that it can be used to represent all major issues related to a policy situation? It must be usable in both graphical and data formats.
Answer
- For examples of using insight networks, see op_fi:Ympäristöterveysindikaattori.
Rationale
Process
| Id | Title | Content | Sign | Target | Type | Paradigm | Relation | Result | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| arg1234 | Short title for display | Actual argument | Signature | arg9876 | relevance | science | attack | 1 | If paradigm changes (all else equal), relation may change, although typically only the result changes. |
| arg1234 | Short title for display | Actual argument | Signature | arg5555 | relevance | science | comment | 0 | |
| arg1234 | Short title for display | Actual argument | Signature | arg6666 | truth | science | defense | 1 | Truth refers to the truth of the target |
| arg1234 | Short title for display | Actual argument | Signature | arg1234 | selftruth | science | attack | 0 | Selftruth refers to the truth of the argument itself, unlike other types that refer to the target. |
| arg1234 | Short title for display | Actual argument | Signature | arg9876 | relevance | toldya | comment | 0 | |
| arg1234 | Short title for display | Actual argument | Signature | arg5555 | relevance | toldya | defense | 1 | |
| arg1234 | Short title for display | Actual argument | Signature | arg6666 | truth | toldya | attack | 0 | |
| arg1234 | Short title for display | Actual argument | Signature | arg1234 | selftruth | toldya | comment | 1 | The relation in case of type=selftruth is irrelevant and is ignored. |
| These are unique to an argument | |||||||||
| These are unique to an argument-target pair | |||||||||
| These are unique to a triple of argument-target-paradigm |
- Insight networks have been described in a scientific article manuscript From open assessment to shared understanding: practical experiences#Insight networks. Objects and their relations used in open policy practice are described on page Open policy ontology.
There is a need for methods facilitating the flow of information and understanding between science and policy. The principle is to describe a risk situation in a formal manner. Insight networks contain items along a causal pathway (or network) from e.g. abatement strategies to emissions to dispersion to exposure to effects. They have been designed to describe also non-causal connections such as non-causal reasoning, values, preferences, and arguments.
These diagrams use graph theory with vertices (or nodes) and arcs (or arrows). They are used to describe and define all the pieces needed for a description of the situation under scrutiny. Diagrams may be produced with any graphics software, providing that calculation functions are not required. If calculations are needed, we recommend the use of R software and OpasnetUtils package.
| Parameter | Css selector (Opasnet page scraping) | Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Id | .argument attr=id | Must start with a letter |
| Title | .argument .title | Short text. Is shown on insight graph as node label |
| Content | .argument .content | Text, may be long. Is shown with hover on graph |
| Sign | .argument .sign a:first-of-type | Must contain a link to participant's user page. Is shown with hover on graph |
| Target | NA | Previous argument one level up, or the statement for arguments on the first level |
| Type | .argument i.type | One of the three: relevance, truth, or selftruth (or "both", which is depreciated) |
| Paradigm | .argument .paradigm | Each paradigm should be described on a dedicated page. The rules implemented must be clear |
| Relation | .argument .relation | Is one of these: attack, defense, comment. "Branches" are typically uninteresting and ignored. |
| Result |
|
Truthlikeness of the relation. Either 1 or 0 |
This is the process how data flows into insight diagrams:
- List of data tables of different insight diagrams is found from https://yhteistyotilat.fi/wiki08/x/1oGxAg. It has the following columns:
- Ilmio: Name of the phenomenon. This will become the name of a csv data file.
- Id: Identifier of the phenomenon. This will be used in Oldid of the items and relations.
- Tyyppi: Type of the table. In practice, it defines the columns that the data table has. Different types are listed on #Types of insight network tables.
- URL: Location of the data table. If the URL contains "google.com", it is assumed to be a google sheet. If the type (Tyyppi) is "keskustelu", it is assumed to be an Opasnet page with discussions. Otherwise, it is assumed to be a table on a web page that can be scraped with read_html() function.
- Taulu: If the data is a table on a web page, it is the number of the table on that page. If the data is a discussion, it is the number of discussion; missing value means that all discussions on that page are read.
- Alkurivi: In case of google sheets, it is the first row with actual data.
- Kuvaus: Description of the table, with possible links to relevant description page.
All data tables and discussions are listed, formatted and saved as csv files in a zip file called op_fi:File:Näkemysverkkojen tietotauluja.zip. From there, the data can be accessed from within Opasnet Rtools. (The code scraping web pages does not work in Opasnet, although it is stored there.) Little formatting is done here, mainly the column titles are standardised. But the number and type of columns is not changed.
In the next phase, each csv file is opened, interpreted, and defined as items and relations. This is done in code Op_fi5810/graphs on page op_fi:Ympäristöterveysindikaattori. All these are saved as a DiagrammeR graph, and each topic may be separately selected as a subgraph.
- 0094: . Are Tehtäväkokonaisuus, Osiotyyppi, JHS-luokka actually types of objects, or are they just indices. Yes, they should be indices and the objects relate to them with "has index". Correct table 4. --Jouni (talk) 20:46, 17 July 2018 (UTC) (type: ; paradigms: science: relevant attack)
- 0095: . Check the code about renderging graphs and creating a server function that also works on non-web environments on op_fi:Keskustelu:Näkemysverkko#Näkemysverkkoabstrakti vaikuttavuuden tutkimuksen päiville 4.-5.12.2018 --Jouni (talk) 20:46, 17 July 2018 (UTC) (type: ; paradigms: science: relevant attack)
Data
Graphical properties of objects and relations
| Obs | Property | Value | Parameter | Result | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | default | default | node.shape | circle | Default values unless something else is specified |
| 2 | default | default | node.sides | 4 | |
| 3 | default | default | node.skew | 0 | |
| 4 | default | default | node.fillcolor | white | |
| 5 | default | default | node.fontsize | 11 | |
| 6 | default | default | node.height | 0.5 | |
| 7 | default | default | node.width | 0.5 | |
| 8 | default | default | node.color | brown | |
| 9 | default | default | node.penwidth | 2 | |
| 10 | default | default | node.fontcolor | black | |
| 11 | default | default | node.distortion | 0 | |
| 12 | default | default | edge.color | grey | |
| 13 | default | default | edge.fontsize | 10 | Not currently used |
| 14 | default | default | edge.fontcolor | grey | |
| 15 | default | default | edge.style | dotted | |
| 16 | default | default | edge.penwidth | 2 | |
| 17 | default | default | edge.arrowsize | 1 | Not currently used |
| 18 | type | unknown | node.fillcolor | yellow | This formatting is used if there are undefined objects |
| 19 | type | unknown | node.color | green | |
| 20 | type | substance | node.shape | circle | Substantive type object |
| 21 | type | substance | node.fillcolor | skyblue2 | Substantive type object |
| 22 | type | knowledge crystal | node.color | gold | Knowledge crystal type object (including ovariables and key ovariables) |
| 23 | type | option | node.color | palevioletred | Option for a decision |
| 24 | type | option | node.fillcolor | white | Option for a decision |
| 25 | type | index | node.shape | polygon | Index or other classifying determinant |
| 26 | type | index | node.sides | 4 | |
| 27 | type | index | node.skew | 0.5 | |
| 28 | type | index | node.fillcolor | purple1 | |
| 29 | type | index | node.height | 0.3 | |
| 30 | type | graph | node.shape | polygon | Index or other classifying determinant |
| 31 | type | graph | node.sides | 3 | |
| 32 | type | graph | node.fillcolor | pink | |
| 33 | type | assessment | node.shape | polygon | Assessment |
| 34 | type | assessment | node.sides | 8 | |
| 35 | type | assessment | node.fillcolor | purple1 | |
| 36 | type | stakeholder | node.shape | hexagon | Stakeholder type object |
| 37 | type | stakeholder | node.fillcolor | khaki1 | Stakeholder type object |
| 38 | type | stakeholder | node.width | 0.8 | Stakeholder type object |
| 39 | type | method | node.shape | polygon | Method type object |
| 40 | type | method | node.sides | 6 | Method type object |
| 41 | type | method | node.fillcolor | purple1 | Method type object |
| 42 | type | process | node.shape | pentagon | Process type object |
| 43 | type | process | node.fillcolor | purple1 | Process type object |
| 44 | type | action | node.fillcolor | pink | Process type object |
| 45 | type | task 1 | node.color | brown | Illustration of the responsible organisation of the task |
| 46 | type | task 2 | node.color | yellow | Illustration of the responsible organisation of the task |
| 47 | type | task 3 | node.color | blue | Illustration of the responsible organisation of the task |
| 48 | type | task 4 | node.color | green | Illustration of the responsible organisation of the task |
| 49 | type | task 5 | node.color | red | Illustration of the responsible organisation of the task |
| 50 | type | decision | node.shape | rectangle | Decision type object |
| 51 | type | decision | node.fillcolor | red | Decision type object |
| 52 | type | data | node.shape | rectangle | Data type object |
| 53 | type | data | node.fillcolor | gold | Data type object |
| 54 | type | objective | node.shape | diamond | Objective type object |
| 55 | type | objective | node.fillcolor | yellow | Objective type object |
| 56 | type | objective | node.width | 0.8 | Objective type object |
| 57 | type | publication | node.fillcolor | gray | Publication type object |
| 58 | type | statement | node.shape | polygon | Argument type object |
| 59 | type | statement | node.sides | 4 | Argument type object |
| 60 | type | statement | node.width | 0.8 | Argument type object |
| 61 | type | statement | node.distortion | -0.5 | Argument type object |
| 62 | type | true statement | node.fillcolor | gold | Argument type object |
| 63 | type | false statement | node.fillcolor | gray | Argument type object |
| 64 | type | fact opening statement | node.fillcolor | lightskyblue1 | Argument type object |
| 65 | type | value opening statement | node.fillcolor | palegreen1 | Argument type object |
| 66 | type | fact closing statement | node.fillcolor | skyblue | Argument type object |
| 67 | type | value closing statement | node.fillcolor | springgreen | Argument type object |
| 68 | type | fact discussion | node.fillcolor | skyblue | Argument type object. Not neede? |
| 69 | type | value discussion | node.fillcolor | springgreen | Value judgement type object. Not needed? |
| 70 | type | risk factor | node.color | pink | Additional information about object class |
| 71 | type | indicator | node.color | brown | Additional information about object class |
| 72 | type | indicator | node.fillcolor | gold | Additional information about object class |
| 73 | type | arviointikriteeri | node.color | orange | Not quite clear what criteria objects are: indicators or value statements, or something else |
| 74 | type | task | node.color | green | Additional information about object class |
| 75 | type | data | node.color | orange | Additional information about object class |
| 76 | type | health organisation | node.color | yellow | Additional information about object class |
| 77 | Relation | causal link | edge.color | black | Causal link |
| 78 | Relation | causal link | edge.style | solid | Causal link |
| 79 | Relation | positive causal link | edge.fontcolor | green | Causal link |
| 80 | Relation | negative causal link | edge.fontcolor | red | Causal link |
| 81 | Relation | participatory link | edge.color | purple | Participatory link |
| 82 | Relation | participatory link | edge.style | dashed | Participatory link |
| 83 | Relation | operational link | edge.color | black | Operational link |
| 84 | Relation | operational link | edge.style | dashed | Operational link |
| 85 | Relation | evaluative link | edge.color | green | Evaluative link |
| 86 | Relation | relevant attack | edge.color | red | Attacking argument |
| 87 | Relation | relevant defense | edge.color | green | Defending argument |
| 88 | Relation | relevant comment | edge.color | blue | Commenting argument |
| 89 | Relation | irrelevant argument | edge.color | gray | Invalid argument |
| 90 | Relation | argumentative link | edge.style | dotted | Argumentative link |
| 91 | Relation | argumentative link | edge.penwidth | 4 | Argumentative link |
| 92 | Relation | referential link | edge.color | red | Referential link |
| 93 | Relation | referential link | edge.style | dashed | Referential link |
Types of insight network tables
| Obs | Type | Column names | Dummy |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | oletus | type, Item, label, Relation, Object, Description, URL | 1 |
| 2 | sotearv | Ikaryhma, AHVK, Item, Teema, Ulottuvuus, Osiotyyppi, Tietolahde, KUVA id, Sotkanet id, JHS-luokka, Ryhman perustelut | 1 |
| 3 | hnh2035 | Teema, Oldid, Item, Ohjelma, Vastuu, Aikajanne, Vaativuus, Kustannukset, Kust.kaupungille, Hyodyt.kaupungille, Kust.muille, Hyodyt.muille, Paastovahenema, Muut.vaikutukset, Seurantaindikaattori, Esimerkki, Description | 1 |
| 4 | kuvaind | Oldid, Item, Teema, Aihe2, Aihe3, Tietopaketti1, Tietopaketti2, Tietopaketti3, Mita.mittaa, Mitta-arvo ja muodostaminen, Tietolahde, Tietolahde ja tausta, Tuotannossa, Tietotarpeen taso, Tuottamistaso, Kansainvaliset tietotoimitukset, Muut kayttotarkoitukset, Description | 1 |
| 5 | sitra100 | Item, Suuruus, Teema, URL | 1 |
| 6 | hvkertomus | Oldid, Item, Teema, Vaestoryhma, Lahde ja muodostaminen, Mita mittaa, KUVA-mittarissa, Hyte-kertoimessa, Arviointiraportissa, Hyvinvointikertomuksessa, Perustelut | 1 |
| 7 | hnhos | Oldid, type, Item, Description | 1 |
| 8 | keskustelu | Oldid, type, Item, label, Relation, Object, Description, URL | 1 |
| 9 | arviointi | Oldid, type, Item, Relation, Object, Description, URL, label | 1 |
Calculations
There are three different identifiers for a subject item.
- Oldid: a technical identifier typically of format context.number, where number is a sequential number within a context.
- Item: the actual name of the item, detailed enough to give a good understanding of its meaning.
- label: a short name shown on insight networks. Does not exmplain everything, just enough to distinguish it from other items.
If Oldid is not given, it is created from the context and a number. If label is not given in data, it is truncated from Item.
Object item has one column Object that may contain any of these. The priority is Item > label > Oldid > Object. The last option means that it is assumed that Object refers to a new item that is not mentioned in the Item column.
An insight network is produced in this order (last object mentioned first).
- gr: a diagrammer graph with all data and formatting for an insight network. Produced by makeInsightGraph.
- makeInsightGraph
Making insight graphs
Fetch data from the web: makeInsightTables function
Insight network
This is an overall ovariable that automatically fetches all dependencies.
Shiny server
Scrape functions
These functions will be placed in the OpasnetUtils package. For now, it must be manually copied to your code.
Copy descriptions to ovariables
The function assessmentDescriptions scans through an assessment ovarible that has all relevant assessment objects as parents. Dependencies slot may also have additional information, such as the following.
- Name: name of parent (obligatory)
- Ident: Opasnet page identifier and code name where the parent object can be loaded (e.g. Op_en7748/hia). Note: This is typically the code for the whole assessment, not the individual codes for the objects.
- Token: Token for the model run where the parent object can be loaded (e.g. xxNsLw5hWdM6xyYp)
- Description: A short description about what the object is. This is typically shown when cursor hovers over the object on an online insight diagram.
- Page: Opasnet page identifier for the object's knowledge crystal page, which contains the research question, answer, and description of the object, together with discussion, if any. Typically this is empty for ovariables, because this information can be found from ovariable@meta slot and there is no need to duplicate it here.
- Child: An object to which this object links. This is typically needed for objects such as graphs and data.frames that do not contain this information in their own structure, unlike ovariables. The direction of a relation is away from this object because then this object is the subject in triple sentences and can be given other parameters as well in other columns. A typical sentence is "graph describes ovariable", but for illustrative purposes this is inversed on insight networks so that the arrow points from an ovariable to a graph ("ovariable is described by graph").
- Other columns are allowed.
Old notation
⇤--#: . Look at the table below together with Open policy ontology and merge. Decide which things should be on this page and which should be on the other. --Jouni (talk) 06:55, 24 April 2018 (UTC) (type: truth; paradigms: science: attack)
Previous notations
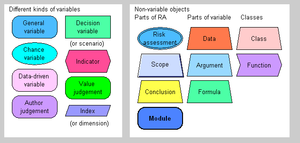
Insight networks have previously been called pyrkilo diagrams, extended causal diagrams, and factor-effect-value networks. These names are no longer in active use. An archived version of the notation can be found from an earlier version of this page.
See also
- Open policy practice
- Open policy ontology
- From open assessment to shared understanding: practical experiences
- Category:Causal diagram