Concentrations of beneficial nutrients in fish: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
(→Fineli) |
||
| (23 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category: Fish]] | |||
[[Category: Concentrations in the environment]] | |||
{{variable|moderator=Olli | |||
| reference = {{publication | |||
| authors = Anna Karjalainen, Jouni T. Tuomisto, Patrycja Gradowska | |||
| page = Concentrations of beneficial nutrients in fish | |||
| explanation = | |||
| publishingyear = 2009 | |||
| urn = | |||
| elsewhere = | |||
}} | |||
}} | |||
== | == Question == | ||
What are the '''concentrations of beneficial nutrients in fish''' (such as omega-3 fatty acids (EPA + DHA + fatty acid 18:3 n-3)) in fish.{{reslink|Should the variable restrict to Finland?}} Concentrations of sea and freshwater fish species are studied separately. | |||
== Answer == | |||
'''Note!''' The first version of results only uses Data 3, for practical reasons (other nutrients than omega-3 are not yet needed). | |||
{{resultlink}} | |||
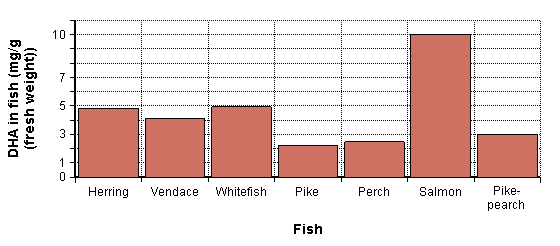
Concentrations of omega-3 fatty acids in fish extracted from <ref name="fineli"/>, where they are indicated as mass units/100 g fish analysed. | [[image:Concentrations of beneficial nutrients in fish.png]] | ||
#one that is presumed as a common one used by the Finnish consumers (roasting), and | |||
== Rationale == | |||
=== Data === | |||
Concentrations of beneficial nutrients in fish extracted from <ref name="fineli"> the Fineli database [http://www.fineli.fi/foodclass.php?classif=fuclass&amp;amp;amp;amp;class=fish&amp;amp;amp;amp;lang=en]</ref>, where they are indicated as mass units/100 g fish analysed. | |||
Concentrations of omega-3 fatty acids in fish extracted from <ref name="fineli" />, where they are indicated as mass units/100 g fish analysed. Criteria for choosing the fish preparation method used prior the analyses: | |||
#one that is presumed as a common one used by the Finnish consumers (roasting), and | |||
#also as available for most of the fish in the database. | #also as available for most of the fish in the database. | ||
The data for omega-3 fatty acids was reported as mean values of the fish species<ref>Omega-3 fatty acids: database of fineli (www.ktlwww.ktl.fi/fineli)</ref>. {{reslink|Omega-3 data}} | |||
*Omega-3 fatty acids, mg/g, as sum of n-3 PUFA (polyunsaturated fatty acids) precursors ALA (alphalinolenic acid), EPA (eicosapanthenic acid), and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid). DPA (docosapentaenoic acid) not available in the database. | |||
*Omega-3 fatty acids, mg/g, as DHA and EPA only. | |||
**Vitamin D, ug/g | |||
**Vitamin E, mg/g | |||
**Selenium, ug/g | |||
**Iodine, ug/g | |||
**Group B vitamins, mg/g, as sum of B1 (tiamin), B2 (riboflavin), B6 (pyridoxin), B12 (cyanokobalamin) and niacin as its eqvivalents NE. {{reslink|Treatment of vitamins B as summed up}} | |||
( | |||
The most commonly consumed fish species are described: Farmed salmon, wild salmon, herring, white fish, sprat, perch, flounder, pike-perch, bream, pike, vendace and burbot. Concentration data for imported fish in Finland is not available in many cases. {{reslink|Number of samples}} | |||
'''Data 1''' | |||
mass units/100 g fish analysed | |||
{|{{prettytable}} | {| {{prettytable}} | ||
! Fish species | |- | ||
! Omega-3-PUFA contents, mg/g | ! Fish species | ||
! Vitamin D, ug/g | ! Omega-3-PUFA contents, mg/g | ||
! Vitamin E, mg/g | ! Vitamin D, ug/g | ||
! Selenium, ug/g | ! Vitamin E, mg/g | ||
! Iodine, ug/g | ! Selenium, ug/g | ||
! Iodine, ug/g | |||
! Group B vitamins, mg/g, | ! Group B vitamins, mg/g, | ||
| | |- | ||
| Baltic herring (Clupea harengus membras) | | Baltic herring (Clupea harengus membras) | ||
| 12.13 | | 12.13 | ||
| 0.17 | | 0.17 | ||
| 0.03 | | 0.03 | ||
| 0.18 | | 0.18 | ||
| 0.45 | | 0.45 | ||
| 0.17 | | 0.17 | ||
| 0.03 | |- | ||
| 0.18 | | Herring (Clupea harengus) | ||
| 0.45 | | 12.13 | ||
| 0.17 | |||
| 0.03 | |||
| 0.18 | |||
| 0.45 | |||
| 0.17 | | 0.17 | ||
| | |- | ||
| Vendace (Coregonus albula) | | Vendace (Coregonus albula) | ||
| 12.77 | | 12.77 | ||
| 0.13 | | 0.13 | ||
| 0.03 | | 0.03 | ||
| 0.22 | | 0.22 | ||
| 0.76 | | 0.76 | ||
| 0.00 | | 0.00 | ||
| | |- | ||
| Whitefish (Coregonus lavaretus) | | Whitefish (Coregonus lavaretus) | ||
| 10.71 | | 10.71 | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | |- | ||
| Pike (Esox lucius) | | Pike (Esox lucius) | ||
| 6.75 | | 6.75 | ||
| 0.03 | | 0.03 | ||
| 0.02 | | 0.02 | ||
| 0.22 | | 0.22 | ||
| 0.34 | | 0.34 | ||
| 0.08 | | 0.08 | ||
| | |- | ||
| Rainbow trout (Onchorhynchus mykiss) | | Rainbow trout (Onchorhynchus mykiss) | ||
| 20.52 | | 20.52 | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | |- | ||
| Shrimp (Pandalus sp.) | | Shrimp (Pandalus sp.) | ||
| 2.49 | | 2.49 | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | |- | ||
| Perch (Perca fluviatilis) | | Perch (Perca fluviatilis) | ||
| 7.17 | | 7.17 | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | |- | ||
| Saithe (Pollachius virens) | | Saithe (Pollachius virens) | ||
| 3.87 | | 3.87 | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | |- | ||
| Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) | | Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) | ||
| 17.42 | | 17.42 | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | |- | ||
| Pike-perch (Sander lucioperca) | | Pike-perch (Sander lucioperca) | ||
| 4.06 | | 4.06 | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | |- | ||
| Tuna (Thunnus thynnus) | | Tuna (Thunnus thynnus) | ||
| 32.67 | | 32.67 | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
|} | |||
'''Data 2''' | |||
*There are no separate data for farmed and for wild salmon. Therefore they are assumed to be the same. | |||
*There are no data for vendace(sea), so assumption is that the parameters are the same as vendace(inland) | |||
*There are no data for bream(sea), so assumption is that the parameters are the same as bream(inland) | |||
*There are no data for wild salmon(inland), so assumption is that the parameters are the same as wildsalmon(sea) | |||
First, the mercury data was used to form lognormal distributions for each species with parameters median and geometric standard deviation. Secondly, the proportion of methylmercury from total mercury was taken into account. Methylmercury proportion is assumed to follow triangular distribution (author judgement) with parameters (min=0.81, mode=0.93,max=0,98). {{reslink|Author judgement about the chosen distribution}} | |||
The omega-3 distributions chosen by author judgement. Concentration distributions were formed according to amount of data. a) If 3 or more data points → triangular distribution, b) if 2 data points → uniform distribution, c) if 1 data point → normal distribution {{reslink|Rationale behind the chosen distribution}} | |||
Sprat: omega-3 concentration(sprat) = omega-3 concentration(herring) closely related species, assumed to have similar composition | |||
Units: mg/kg in fresh weight | |||
{| {{prettytable}} | |||
|- | |||
! Fish species | |||
! Omega-3 concentration | |||
|- | |||
| Farmed salmon (sea+inland) | |||
| 1.553e+004 | |||
|- | |||
| Wild salmon | |||
| 1.516e+004 | |||
|- | |||
| Herring(sea) | |||
| 9790 | |||
|- | |||
| White fish(sea) | |||
| 7830 | |||
|- | |||
| Sprat(sea) | |||
| 9790 | |||
|- | |||
| Perch(sea) | |||
| 3030 | |||
|- | |||
| Flounder(sea) | |||
| 4220 | |||
|- | |||
| Pike-perch(sea) | |||
| 4060 | |||
|- | |||
| Bream(sea) | |||
| 4930 | |||
|- | |||
| Pike(sea) | |||
| 2920 | |||
|- | |||
| Vendace(sea) | |||
| 7510 | |||
|- | |||
| Burbot(sea) | |||
| 2010 | |||
|- | |||
| Wild salmon(inland) | |||
| 1.504e+004 | |||
|- | |||
| White fish(inland) | |||
| 7830 | |||
|- | |||
| Perch(inland) | |||
| 3030 | |||
|- | |||
| Pike-perch(inland) | |||
| 4060 | |||
|- | |||
| Bream(inland) | |||
| 4930 | |||
|- | |||
| Pike(inland) | |||
| 2920 | |||
|- | |||
| Vendace(inland) | |||
| 7510 | |||
|- | |||
| Burbot(inland) | |||
| 2010 | |||
|} | |} | ||
'''Data 3''' | |||
Since there are only mean concentration values available exponential distribution has been chosen to model the concentration of DHA and concentration of EPA in various sea and inland fish species. | |||
Moreover, the Fineli database<ref name="fineli" /> provides concentrations of nutrients in species caught mostly in the Baltic Sea (except vendace which was caught in inland waters). Thus, the concentration data for some of the species chosen is not available. Therefore, it has been assumed that the DHA (EPA) concentration in sea and freshwater species is the same. | |||
Units: mg/g fish | |||
{| {{prettytable}} | |||
|- | |||
| '''Fish species''' | |||
| '''Mean DHA concentration''' | |||
| '''Mean EPA concentration''' | |||
|- | |||
| Baltic Herring | |||
| 4.82 | |||
| 2.27 | |||
|- | |||
| Vendace(inland) | |||
| 4.09 | |||
| 2.06 | |||
|- | |||
| Vendace(sea) | |||
| 4.09 | |||
| 2.06 | |||
|- | |||
| Whitefish(inland) | |||
| 4.93 | |||
| 2.63 | |||
|- | |||
| Whitefish(sea) | |||
| 4.93 | |||
| 2.63 | |||
|- | |||
| Pike(inland) | |||
| 2.17 | |||
| 0.44 | |||
|- | |||
| Pike(sea) | |||
| 2.17 | |||
| 0.44 | |||
|- | |||
| Perch(inland) | |||
| 2.45 | |||
| 0.54 | |||
|- | |||
| Perch(sea) | |||
| 2.45 | |||
| 0.54 | |||
|- | |||
| Atlantic Salmon | |||
| 10.02 | |||
| 3.45 | |||
|- | |||
| Pike-perch(inland) | |||
| 3.01 | |||
| 0.92 | |||
|- | |||
| Pike-perch(sea) | |||
| 3.01 | |||
| 0.92 | |||
|} | |||
==== Fineli ==== | |||
Data comes from [https://fineli.fi Fineli database] maintained by [[THL]]. | |||
{| {{prettytable}} | |||
|+'''Concentrations of fatty acid concentrations in salmon[https://fineli.fi/fineli/fi/elintarvikkeet?q=lohi] and herring[https://fineli.fi/fineli/fi/elintarvikkeet?q=silakka] products (g/100 g) (2017 data) | |||
!Salmon product !! Omega-3 !! ALA (alphalinolenic acid) !! EPA !! DHA !! Vitamin D (µg) | |||
|--- | |||
| Salmon, farmed || 2.3 || 0.796 || 0.456 || 0.669 || 6.7 | |||
|--- | |||
| Salmon, whole || 2.7 || 0.176 || 0.504 || 1.465 || 5.2 | |||
|--- | |||
| Salmon filet || 4.2 || 0.270 || 0.775 || 2.253 || 8.0 | |||
|--- | |||
| Salmon filet, cold smoked || 1.4 || 0.470 || 0.286 || 0.412 || 7.2 | |||
|--- | |||
| Salmon filet, fried ("paistettu") || 4.7 || 0.367 || 0.842 || 2.449 || 8.7 | |||
|--- | |||
| Salmon filet, baked in oven || 4.9 || 0.314 || 0.901 || 2.620 || 9.3 | |||
|--- | |||
| Herring filet || 2.4 || 0.174 || 0.413 || 0.586 || 17.9 | |||
|--- | |||
| Herring, fresh || 1.4 || 0.125 || 0.402 || 0.606 || 15.6 | |||
|--- | |||
| Herring, smoked || 1.8 || 0.154 || 0.495 || 0.745 || 17.0 | |||
|} | |||
<t2b name="Fineli summary" index="Fish,Exposure_agent" unit="mg/ 100 g"> | |||
Herring|ALA|154 (125 - 174) | |||
Salmon|ALA|470 (176 - 796) | |||
Salmon|D_vitamin|0.0075 +- 0.0015 | |||
Salmon|DHA|1600 +- 950 | |||
Salmon|EPA|630 +- 250 | |||
Salmon|Omega3|3400 +- 1400 | |||
</t2b> | |||
<t2b name="Fineli data for common fish species" index="Kala,Fish,Nutrient" locations="energia laskennallinen (kJ),rasva (g),proteiini (g),rasvahapot yhteensä (g),rasvahapot moni-tyydyttymättömät (g),rasvahapot yksittäis-tyydyttymättömät cis (g),rasvahapot tyydyttyneet (g),rasvahapot trans (g),rasvahapot n-3 moni-tyydyttymättömät (g),rasvahapot n-6 moni-tyydyttymättömät (g),rasvahappo 18:2 cis n-6 (linolihappo) (mg),rasvahappo 18:3 n-3 (alfalinoleenihappo) (mg),rasvahappo 20:5 n-3 (EPA) (mg),rasvahappo 22:6 n-3 (DHA) (mg),jodidi (jodi) (µg),fosfori (mg),seleeni (µg),sinkki (mg),D-vitamiini (µg)" unit="several"> | |||
Hauki|Pike|339|0.4|19|0.3|<0.1|<0.1|0.1|<0.1|<0.1|<0.1|11|8|18|30|46.7|240|22|1.1|2.1 | |||
Kala, keskiarvo, silakka/muikku/ahven/hauki|Average fish|413|2.8|18.2|2.3|0.9|0.7|0.7|<0.1|0.7|0.2|101|69|187|254|30|252|24.8|1.8|10.5 | |||
Kirjolohi, filee, kasvatettu|Rainbow trout|715|10.3|19.7|9.6|3.3|4.7|1.5|<0.1|1.8|1.4|1326|481|318|757|6|260|15.1|0.4|5.1 | |||
Lahna|Bream|412|3.2|17.3|2.2|0.7|1|0.5|0|0.6|0.1|35|22|199|273|7|210|28|0.5|14 | |||
Lohi, filee, kasvatettu|Salmon|946|16.4|20|15.1|4.7|8.1|2.3|0.1|2.3|2.2|2055|796|456|669|6.1|240|11.6|0.4|6.7 | |||
Muikku, järvi|Vendace|463|3.9|18.7|2.8|1.3|0.6|0.9|<0.1|1|0.3|102|135|288|300|25.9|290|22|4|9.4 | |||
Siika, kasvatettu|Whitefish|554|5.9|19.8|5.3|1.6|2.6|1|<0.1|1|0.7|574|222|204|394|6.2|248|24.9|0.4|14.4 | |||
Silakkafilee|Herring|601|8.9|16|8.1|3.4|2.6|2|0|2.4|0.9|472|174|413|586|52.4|200|27.1|2.4|15.6 | |||
Särki|Roach|397|2.4|18.2|1.7|0.5|0.8|0.3|0|0.5|<0.1|18|10|112|287|30|252|24.8|1.8|10 | |||
</t2b> | |||
=== Calculations === | |||
==== Bayes model ==== | |||
* Model run 2.3.2017 [http://en.opasnet.org/en-opwiki/index.php?title=Special:RTools&id=9aXDKdIaq4jHrb7e] | |||
* Model run 3.3.2017 with multivariate normal and predictions [http://en.opasnet.org/en-opwiki/index.php?title=Special:RTools&id=W4mWVsEdolRCeTet] | |||
* Model run 19.5.2017 with only vit.param stored [http://en.opasnet.org/en-opwiki/index.php?title=Special:RTools&id=eDNkNIVqTUCnJR62] | |||
<rcode name="bayes" label="Initiate Bayes model (for developers only)" graphics=1> | |||
# This is code Op_en1838/bayes on page [[Concentrations of beneficial nutrients in fish]] | |||
library(OpasnetUtils) | |||
library(rjags) | |||
library(reshape2) | |||
library(ggplot2) | |||
library(car) # For scatterplotMatrix() | |||
dat <- opbase.data("Op_en1838", subset = "Balticherring") | |||
dat$Result <- as.numeric(gsub(",", ".", as.character(dat$Result))) | |||
colnames(dat) | |||
fisl <- sort(unique(as.character(dat$Fish_species))) | |||
compl <- sort(unique(as.character(dat$variable))) | |||
dat.wide <- reshape( | |||
dat, | |||
idvar = "Sample_code", | |||
v.names = "Result", | |||
timevar = "variable", | |||
direction = "wide" | |||
) | |||
mod <- textConnection(" | |||
model{ | |||
for(i in 1:N) { # Observation | |||
conc[i,1:C] ~ dmnorm(mu[], Omega[,]) | |||
} | |||
mu[1:C] ~ dmnorm(mu0[1:C], S2[1:C,1:C]) | |||
Omega[1:C,1:C] ~ dwish(S3[1:C,1:C],4) | |||
conc.pred[1:C] ~ dmnorm(mu[1:C], Omega[1:C,1:C]) | |||
} | |||
") | |||
jags <- jags.model( | |||
mod, | |||
data = list( | |||
N = nrow(dat.wide), | |||
C = length(compl), | |||
conc = dat.wide[ncol(dat.wide)+(-3:0)], | |||
mu0 = rep(100,4), | |||
S2 = diag(4)/100000, | |||
S3 = diag(4)/10000 | |||
), | |||
n.chains = 4, | |||
n.adapt = 100 | |||
) | |||
update(jags, 100) | |||
samps.j <- jags.samples( | |||
jags, | |||
c('mu', 'Omega', 'conc.pred'), | |||
1000 | |||
) | |||
js <- array( | |||
c( | |||
samps.j$mu[,,1], | |||
samps.j$Omega[,1,,1], | |||
samps.j$Omega[,2,,1], | |||
samps.j$Omega[,3,,1], | |||
samps.j$Omega[,4,,1], | |||
samps.j$conc.pred[,,1] | |||
), | |||
dim = c(4,1000,6), | |||
dimnames = list( | |||
Exposure_agent = compl, | |||
Iter = 1:1000, | |||
Parameter = c("mu","Omega1", "Omega2", "Omega3", "Omega4", "conc.pred") | |||
) | |||
) | |||
# Mu for all questions | |||
scatterplotMatrix(t(js[,,1])) | |||
# All parameters for Exposure_agent 1 (DHA?) | |||
scatterplotMatrix(js[1,,]) | |||
jsd <- melt(js) | |||
coda.j <- coda.samples( | |||
jags, | |||
c('mu', 'Omega', 'conc.pred'), | |||
1000 | |||
) | |||
plot(coda.j) | |||
######## vit.param contains expected values of the distribution parameters from the model | |||
vit.param <- list( | |||
mu = apply(js[,,1], MARGIN = 1, FUN = mean), | |||
Omega = solve(apply(js[,,2:5], MARGIN = c(1,3), FUN = mean)) | |||
# solve matrix: precision->covariace | |||
) | |||
objects.store(vit.param) | |||
cat("List vit.param stored.\n") | |||
if(FALSE) { | |||
concddeo.mu <- array( | |||
samps$mu, | |||
dim = c(length(compl), 1000, 4), | |||
dimnames = list(Compound = compl, Iter = 1:1000, Seed = 1:4) | |||
) | |||
concddeo.Omega <- array( | |||
samps$Omega, | |||
dim = c(length(compl), length(compl), 1000, 4), | |||
dimnames = list(Compound1 = compl, Compound2 = compl, Iter = 1:1000, Seed = 1:4) | |||
) | |||
concddeo.pred <- array( | |||
samps$mu, | |||
dim = c(length(compl), 1000, 4), | |||
dimnames = list(Compound = compl, Iter = 1:1000, Seed = 1:4) | |||
) | |||
concdf.mu <- melt(concddeo.mu) | |||
scatterplotMatrix(t(concddeo.mu[,,1])) | |||
concdf.pred <- melt(concddeo.pred) | |||
scatterplotMatrix(t(concddeo.pred[,,1])) | |||
ggplot(dat, aes(x = Result, colour = Fish_species))+geom_density()+ | |||
facet_wrap(~ variable, scales = "free") | |||
ggplot(concdf.pred, aes(x = value))+geom_density()+ | |||
facet_wrap(~ Compound, scales = "free") | |||
objects.store(concddeo.mu, concddeo.Omega, concddeo.pred) | |||
cat("Arrays of concentrations of vitamin D, DHA, EPA, and Omega3) stored:\n") | |||
cat("concddeo.mu (mean), concddeo.Omega (precision matrix), concddeo.pred (predicted distribution).\n") | |||
} #if(FALSE) | |||
</rcode> | |||
==== Initiate ovariable conc_vit ==== | |||
* Initiation 19.5.2017 [http://en.opasnet.org/en-opwiki/index.php?title=Special:RTools&id=xcbB77mKIo3gQUCv] | |||
* Initiation 5.10.2017: salmon data taken from Fineli [http://en.opasnet.org/en-opwiki/index.php?title=Special:RTools&id=TjeHDHy5tFXGI6uq] | |||
* Initiation 3.9.2019 with ALA [http://en.opasnet.org/en-opwiki/index.php?title=Special:RTools&id=gSFr9qInLEXMbhBl] | |||
<rcode name="initiate" label="Initiate conc_vit (for developers only)" embed=1> | |||
# This is code Op_en1838/initiate on page [[Concentrations of beneficial nutrients in fish]] | |||
library(OpasnetUtils) | |||
conc_vit <- Ovariable( | |||
"conc_vit", | |||
ddata = "Op_en1838", | |||
subset="Fineli summary", | |||
dependencies = data.frame(Name = "vit.param", Ident = "Op_en1838/bayes"), | |||
formula = function(...) { | |||
require(MASS) | |||
require(reshape2) | |||
N <- openv$N | |||
vit <- data.frame( | |||
Fish = "Herring", | |||
Iter = 1:N, | |||
as.data.frame(mvrnorm(N, vit.param$mu, vit.param$Omega)) | |||
) | |||
vit <- melt(vit, id.vars = c("Iter", "Fish"), variable.name = "Exposure_agent", value.name = "Result") | |||
return(vit) | |||
}, | |||
unit = "mg /100 g" | |||
) | |||
objects.store(conc_vit) | |||
cat("Ovariable conc_vit stored.\n") | |||
</rcode> | |||
== See also == | |||
* Previous Analytica formulas can be found from a [http://en.opasnet.org/en-opwiki/index.php?title=Concentrations_of_beneficial_nutrients_in_fish&oldid=9672 previous version of this page]. | |||
== References == | |||
<references/> | <references /> | ||
[[Category:THL publications 2010]]<!-- __OBI_TS:1476877071 --> | |||
Latest revision as of 07:31, 12 March 2020
| [show] |
|---|
Question
What are the concentrations of beneficial nutrients in fish (such as omega-3 fatty acids (EPA + DHA + fatty acid 18:3 n-3)) in fish.R↻ Concentrations of sea and freshwater fish species are studied separately.
Answer
Note! The first version of results only uses Data 3, for practical reasons (other nutrients than omega-3 are not yet needed).
{{#opasnet_base_link:Op_en1838}}
Rationale
Data
Concentrations of beneficial nutrients in fish extracted from [1], where they are indicated as mass units/100 g fish analysed.
Concentrations of omega-3 fatty acids in fish extracted from [1], where they are indicated as mass units/100 g fish analysed. Criteria for choosing the fish preparation method used prior the analyses:
- one that is presumed as a common one used by the Finnish consumers (roasting), and
- also as available for most of the fish in the database.
The data for omega-3 fatty acids was reported as mean values of the fish species[2]. R↻
- Omega-3 fatty acids, mg/g, as sum of n-3 PUFA (polyunsaturated fatty acids) precursors ALA (alphalinolenic acid), EPA (eicosapanthenic acid), and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid). DPA (docosapentaenoic acid) not available in the database.
- Omega-3 fatty acids, mg/g, as DHA and EPA only.
- Vitamin D, ug/g
- Vitamin E, mg/g
- Selenium, ug/g
- Iodine, ug/g
- Group B vitamins, mg/g, as sum of B1 (tiamin), B2 (riboflavin), B6 (pyridoxin), B12 (cyanokobalamin) and niacin as its eqvivalents NE. R↻
The most commonly consumed fish species are described: Farmed salmon, wild salmon, herring, white fish, sprat, perch, flounder, pike-perch, bream, pike, vendace and burbot. Concentration data for imported fish in Finland is not available in many cases. R↻
Data 1
mass units/100 g fish analysed
| Fish species | Omega-3-PUFA contents, mg/g | Vitamin D, ug/g | Vitamin E, mg/g | Selenium, ug/g | Iodine, ug/g | Group B vitamins, mg/g, |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baltic herring (Clupea harengus membras) | 12.13 | 0.17 | 0.03 | 0.18 | 0.45 | 0.17 |
| Herring (Clupea harengus) | 12.13 | 0.17 | 0.03 | 0.18 | 0.45 | 0.17 |
| Vendace (Coregonus albula) | 12.77 | 0.13 | 0.03 | 0.22 | 0.76 | 0.00 |
| Whitefish (Coregonus lavaretus) | 10.71 | |||||
| Pike (Esox lucius) | 6.75 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.22 | 0.34 | 0.08 |
| Rainbow trout (Onchorhynchus mykiss) | 20.52 | |||||
| Shrimp (Pandalus sp.) | 2.49 | |||||
| Perch (Perca fluviatilis) | 7.17 | |||||
| Saithe (Pollachius virens) | 3.87 | |||||
| Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) | 17.42 | |||||
| Pike-perch (Sander lucioperca) | 4.06 | |||||
| Tuna (Thunnus thynnus) | 32.67 |
Data 2
- There are no separate data for farmed and for wild salmon. Therefore they are assumed to be the same.
- There are no data for vendace(sea), so assumption is that the parameters are the same as vendace(inland)
- There are no data for bream(sea), so assumption is that the parameters are the same as bream(inland)
- There are no data for wild salmon(inland), so assumption is that the parameters are the same as wildsalmon(sea)
First, the mercury data was used to form lognormal distributions for each species with parameters median and geometric standard deviation. Secondly, the proportion of methylmercury from total mercury was taken into account. Methylmercury proportion is assumed to follow triangular distribution (author judgement) with parameters (min=0.81, mode=0.93,max=0,98). R↻
The omega-3 distributions chosen by author judgement. Concentration distributions were formed according to amount of data. a) If 3 or more data points → triangular distribution, b) if 2 data points → uniform distribution, c) if 1 data point → normal distribution R↻
Sprat: omega-3 concentration(sprat) = omega-3 concentration(herring) closely related species, assumed to have similar composition
Units: mg/kg in fresh weight
| Fish species | Omega-3 concentration |
|---|---|
| Farmed salmon (sea+inland) | 1.553e+004 |
| Wild salmon | 1.516e+004 |
| Herring(sea) | 9790 |
| White fish(sea) | 7830 |
| Sprat(sea) | 9790 |
| Perch(sea) | 3030 |
| Flounder(sea) | 4220 |
| Pike-perch(sea) | 4060 |
| Bream(sea) | 4930 |
| Pike(sea) | 2920 |
| Vendace(sea) | 7510 |
| Burbot(sea) | 2010 |
| Wild salmon(inland) | 1.504e+004 |
| White fish(inland) | 7830 |
| Perch(inland) | 3030 |
| Pike-perch(inland) | 4060 |
| Bream(inland) | 4930 |
| Pike(inland) | 2920 |
| Vendace(inland) | 7510 |
| Burbot(inland) | 2010 |
Data 3
Since there are only mean concentration values available exponential distribution has been chosen to model the concentration of DHA and concentration of EPA in various sea and inland fish species.
Moreover, the Fineli database[1] provides concentrations of nutrients in species caught mostly in the Baltic Sea (except vendace which was caught in inland waters). Thus, the concentration data for some of the species chosen is not available. Therefore, it has been assumed that the DHA (EPA) concentration in sea and freshwater species is the same.
Units: mg/g fish
| Fish species | Mean DHA concentration | Mean EPA concentration |
| Baltic Herring | 4.82 | 2.27 |
| Vendace(inland) | 4.09 | 2.06 |
| Vendace(sea) | 4.09 | 2.06 |
| Whitefish(inland) | 4.93 | 2.63 |
| Whitefish(sea) | 4.93 | 2.63 |
| Pike(inland) | 2.17 | 0.44 |
| Pike(sea) | 2.17 | 0.44 |
| Perch(inland) | 2.45 | 0.54 |
| Perch(sea) | 2.45 | 0.54 |
| Atlantic Salmon | 10.02 | 3.45 |
| Pike-perch(inland) | 3.01 | 0.92 |
| Pike-perch(sea) | 3.01 | 0.92 |
Fineli
Data comes from Fineli database maintained by THL.
| Salmon product | Omega-3 | ALA (alphalinolenic acid) | EPA | DHA | Vitamin D (µg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salmon, farmed | 2.3 | 0.796 | 0.456 | 0.669 | 6.7 |
| Salmon, whole | 2.7 | 0.176 | 0.504 | 1.465 | 5.2 |
| Salmon filet | 4.2 | 0.270 | 0.775 | 2.253 | 8.0 |
| Salmon filet, cold smoked | 1.4 | 0.470 | 0.286 | 0.412 | 7.2 |
| Salmon filet, fried ("paistettu") | 4.7 | 0.367 | 0.842 | 2.449 | 8.7 |
| Salmon filet, baked in oven | 4.9 | 0.314 | 0.901 | 2.620 | 9.3 |
| Herring filet | 2.4 | 0.174 | 0.413 | 0.586 | 17.9 |
| Herring, fresh | 1.4 | 0.125 | 0.402 | 0.606 | 15.6 |
| Herring, smoked | 1.8 | 0.154 | 0.495 | 0.745 | 17.0 |
| Obs | Fish | Exposure_agent | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Herring | ALA | 154 (125 - 174) |
| 2 | Salmon | ALA | 470 (176 - 796) |
| 3 | Salmon | D_vitamin | 0.0075 +- 0.0015 |
| 4 | Salmon | DHA | 1600 +- 950 |
| 5 | Salmon | EPA | 630 +- 250 |
| 6 | Salmon | Omega3 | 3400 +- 1400 |
| Obs | Kala | Fish | energia laskennallinen (kJ) | rasva (g) | proteiini (g) | rasvahapot yhteensä (g) | rasvahapot moni-tyydyttymättömät (g) | rasvahapot yksittäis-tyydyttymättömät cis (g) | rasvahapot tyydyttyneet (g) | rasvahapot trans (g) | rasvahapot n-3 moni-tyydyttymättömät (g) | rasvahapot n-6 moni-tyydyttymättömät (g) | rasvahappo 18:2 cis n-6 (linolihappo) (mg) | rasvahappo 18:3 n-3 (alfalinoleenihappo) (mg) | rasvahappo 20:5 n-3 (EPA) (mg) | rasvahappo 22:6 n-3 (DHA) (mg) | jodidi (jodi) (µg) | fosfori (mg) | seleeni (µg) | sinkki (mg) | D-vitamiini (µg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hauki | Pike | 339 | 0.4 | 19 | 0.3 | <0.1 | <0.1 | 0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | 11 | 8 | 18 | 30 | 46.7 | 240 | 22 | 1.1 | 2.1 |
| 2 | Kala, keskiarvo, silakka/muikku/ahven/hauki | Average fish | 413 | 2.8 | 18.2 | 2.3 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.7 | <0.1 | 0.7 | 0.2 | 101 | 69 | 187 | 254 | 30 | 252 | 24.8 | 1.8 | 10.5 |
| 3 | Kirjolohi, filee, kasvatettu | Rainbow trout | 715 | 10.3 | 19.7 | 9.6 | 3.3 | 4.7 | 1.5 | <0.1 | 1.8 | 1.4 | 1326 | 481 | 318 | 757 | 6 | 260 | 15.1 | 0.4 | 5.1 |
| 4 | Lahna | Bream | 412 | 3.2 | 17.3 | 2.2 | 0.7 | 1 | 0.5 | 0 | 0.6 | 0.1 | 35 | 22 | 199 | 273 | 7 | 210 | 28 | 0.5 | 14 |
| 5 | Lohi, filee, kasvatettu | Salmon | 946 | 16.4 | 20 | 15.1 | 4.7 | 8.1 | 2.3 | 0.1 | 2.3 | 2.2 | 2055 | 796 | 456 | 669 | 6.1 | 240 | 11.6 | 0.4 | 6.7 |
| 6 | Muikku, järvi | Vendace | 463 | 3.9 | 18.7 | 2.8 | 1.3 | 0.6 | 0.9 | <0.1 | 1 | 0.3 | 102 | 135 | 288 | 300 | 25.9 | 290 | 22 | 4 | 9.4 |
| 7 | Siika, kasvatettu | Whitefish | 554 | 5.9 | 19.8 | 5.3 | 1.6 | 2.6 | 1 | <0.1 | 1 | 0.7 | 574 | 222 | 204 | 394 | 6.2 | 248 | 24.9 | 0.4 | 14.4 |
| 8 | Silakkafilee | Herring | 601 | 8.9 | 16 | 8.1 | 3.4 | 2.6 | 2 | 0 | 2.4 | 0.9 | 472 | 174 | 413 | 586 | 52.4 | 200 | 27.1 | 2.4 | 15.6 |
| 9 | Särki | Roach | 397 | 2.4 | 18.2 | 1.7 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.3 | 0 | 0.5 | <0.1 | 18 | 10 | 112 | 287 | 30 | 252 | 24.8 | 1.8 | 10 |
Calculations
Bayes model
- Model run 2.3.2017 [5]
- Model run 3.3.2017 with multivariate normal and predictions [6]
- Model run 19.5.2017 with only vit.param stored [7]
Initiate ovariable conc_vit
- Initiation 19.5.2017 [8]
- Initiation 5.10.2017: salmon data taken from Fineli [9]
- Initiation 3.9.2019 with ALA [10]
See also
- Previous Analytica formulas can be found from a previous version of this page.
References
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 1.2 the Fineli database [1]
- ↑ Omega-3 fatty acids: database of fineli (www.ktlwww.ktl.fi/fineli)