Societal Wellbeing
| Moderator:Jouni (see all) |
|
|
| Upload data
|
| Main message: |
|---|
| Question:
what are the important areas to Societal Well-being ? measurement of social, economic and environmental dimensions is way to develop the concern of social well-being. |
it is difficult to identify how the wellbeing of society is evolving, and how it should be measured. it is clear that societal wellbeing measures should include social, economic and environmental dimensions. On 19 July last year, 68 countries joined the Kingdom of Bhutan in co-sponsoring a resolution titled “Happiness: Towards a holistic approach to development,” which was adopted by consensus by the 193-member UN General Assembly. However, is relevant data available to provide a comprehensive depiction for the UK and crucially, to be able to see how wellbeing overall is changing overtime?
Purpose
Government and non-government officials, politicians, leading economists, scholars, academics and religious leaders are expected to gather to discuss methods the Bhutanese government proposed towards obtaining gross national happiness [1]
- The draft outcome of the meeting includes a report containing a synthesis of discussions, thoughts, views and recommendations following the meeting to be submitted to the UN secretary general, who will then share it with all UN member states.
- Governments worldwide take immediate steps to adopting the new wellbeing and an economic paradigm based on sustainability.
- Recommendations for inclusion into policies the principles of the new economy government worldwide could consider for voluntary adoption were also suggested.
- Promotion of green technologies and poverty alleviation and investments in sustainable infrastructure, like support for green businesses, renewable energy, clean technology and energy efficiency.
Suggestion
Recommendation was developed for inclusion into policies the principles of the new economy government worldwide could consider for voluntary adoption were suggested. The suggestions include
- Promotion of green technologies and poverty alleviation and investments in sustainable infrastructure, like support for green businesses, renewable energy, clean technology and energy efficiency.
- Banning advertising to children to dismantle incentives to excessive consumption, and for governments to introduce work sharing policies that reduce overwork, increase leisure time and prevent layoffs.
- Government procurement from local, organic and fair trade sources, to encourage local economies, and fair trade systems that promote sustainable production methods and fair returns to producers.
- Need to value non-market assets and services to measure progress more accurately and comprehensively, through creation of accounts that value natural, cultural, human and social dynamics.
- Need for ecological tax reforms that tax pollution and depletion of natural capital.
Societal Well-being at Great Britain
The UK government is poised to start measuring people's psychological and environmental wellbeing, bidding to be among the first countries to officially monitor happiness.
Despite "nervousness" in Downing Street at the prospect of testing the national mood amid deep cuts and last week's riot in Westminster, the Office of National Statistics will shortly be asked to produce measures to implement David Cameron's long-stated ambition of gauging "general wellbeing".
UK aims to identify key components of wellbeing and explore existing datasets that could help build a picture of societal wellbeing, quality of life and progress in the UK.
Intended users
* Intended users are those for whom the assessment is made.
Participants
* Participants are those who may participate in the making of the assessment.
The minimum group of people for a successful assessment is always described.
If some groups must be excluded, this must be explicitly motivated.
Definition
Upload a causal diagram and change the right name here.
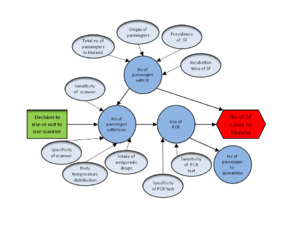
Decision variables
* Decision variables: decisions that are considered.
Indicators
* Indicators: outcome variables of interest.
Value variables
* Value variables: value judgements (usually about indicators).
Other variables
* Other variables: any variables that link to the causal network and are within the boundaries of the assessment.
Analyses
* Analyses: statistical and other analyses that contain two or more variables, e.g. optimizing.
Indices
* Indices: lists of particular locations along spatial, temporal, or other dimensions.
Result
* Results of indicators and assessment-specific analyses.
Results
Conclusions
* Conclusions are based on the results, given the scope.