Excess cases of iMetHb in England and Wales: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Scope== | == Scope== | ||
Excess risk of iMetHb attributable to nitrates in drinking water | Excess risk of iMetHb attributable to nitrates in drinking water | ||
| Line 21: | Line 20: | ||
== Result == | == Result == | ||
<gallery> | |||
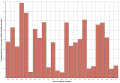
Image:Excess cases of ime uk.PNG|'''Figure 1''' - Medians of excess cased of iMetHb in England & Wales | |||
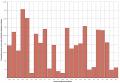
Image:Excess rate of imet uk.PNG|'''Figure 2''' - Medians of excess rate of iMetHb in England & Wales | |||
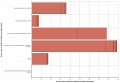
Image:Excess cases imethb importance.png|'''Figure 3''' - Importance analysis of excess cased of iMetHb in England & Wales | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 07:50, 5 September 2008
Scope
Excess risk of iMetHb attributable to nitrates in drinking water
Definition
Causality
- Population age structure per country
- Infants <6 monts
- Excess rate of iMetHb
- Background prevalenxe of iMetHb
Formula
Analytica_id:
<anacode>Excess_rate_of_imeth*Infants__6_months</anacode>
Unit
NA
Result
-
Figure 1 - Medians of excess cased of iMetHb in England & Wales
-
Figure 2 - Medians of excess rate of iMetHb in England & Wales
-
Figure 3 - Importance analysis of excess cased of iMetHb in England & Wales