User:Tine Bizjak: Difference between revisions
Tine Bizjak (talk | contribs) |
Tine Bizjak (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 234: | Line 234: | ||
==Homework 5== | ==Homework 5== | ||
Homework done in a pair. See page of [[User:Tamara Gajst#Homework 5|Tamara]] | Homework done in a pair. See page of [[User:Tamara Gajst#Homework 5|Tamara]] | ||
==Homework 6== | |||
Revision as of 08:46, 6 June 2017
Decision analysis and risk management 2017
Homework 1
←--#: . Very good! --Jouni (talk) 08:40, 10 April 2017 (UTC) (type: truth; paradigms: science: defence)
Homework 1a: Open policy practice
2. What is shared understanding?
Shared understanding is achieved when all participants of a decision making process understand:
- considered decision options and their outcomes,
- pursued objectives,
- existing facts, opinions and disagreements and
- selection of particular decision option.
Shared understanding is written down and shared with everyone.
9. What are the dimensions of openness?
Dimensions of openness can be used to find out if the work deviates from the openness ideal. They can identify how the openness can make a difference. Dimensions of openness include:
- Scope of participation (who can participate?)
- Access to information (for participants)
- Timing of openness (when can participants participate)
- Scope of contribution (to which parts can participants contribute)
- Impact of contribution (influence of participants contributions?)
18. What parts does the open policy practice consist of?
Open policy practice consists of:
- shared understanding – for all participants (the goal of open policy practice)
- execution (collecting, organising and synthesising scientific knowledge, values); 6 principles (intentionality, causality,critique, shared information objects, openness, reuse)
- evaluation and management (happening before, during and after execution)
- co-creation skills and facilitation or interactional expertise (to organization and synthesis of information)
Source: [Open policy practice]
Homework 1b: Learn the terms in Quizlet
Checked all 5 Quizlet topics. I looked at the flashcards, did tests and matched the terms with their meanings.
Homework 1c: Introduction to critical thinking
Checked some of the videos and did excercises.
Homework 1d: Introduction to probabilities
Checked the content on Khan academy.
Homework 2: Basic skills of open policy practice
Homework 3: Basic concepts of open assessment and co-creation
Task A
Question 1: I have come across the term bootstrap in relation with statistical tests before and am still not sure when this technique is applicable? ----#: . Zahra Shirani also asked about bootstrap, so see my answer to him. This technique is applicable for example estimating confidence intervals based on a single data set. --Jouni (talk) 09:27, 20 April 2017 (UTC) (type: truth; paradigms: science: comment)
Question 2: The definition of multinomial is not very clear. Does it refer to animals or individuals that can be classified into categories? ----#: . Multinomial refers to distributions that are an extension to binomial distribution. Binomial distribution describes a process, where you repeat a trial that has exactly two possible outcomes, such as tossing a coin. With n trials and probability of success p, binomial distribution describes how likely it is to get k successes out of n. Multinomial is the same except there are more than two possible outcomes, and each of them has a certain probability to occur. It is like a multi-sided dice. --Jouni (talk) 09:27, 20 April 2017 (UTC) (type: truth; paradigms: science: comment)
Task B
←--#: . Great! --Jouni (talk) 06:22, 11 May 2017 (UTC) (type: truth; paradigms: science: defence)
What is co-creation?
Co-creation is describing a process when all or most of the stakeholders are somehow involved in the making of a final “product”. The term can be applied in different areas. In case of a consumer – producer relationship it can describe a process when the consumers actively participate in the product design, development, purpose etc. The company producing a product is not designing it on its own, like it was done traditionally. In co-creation the value creation is done jointly by the company and the customer, which allows the customer to influence the construction so it will suit him better (it does not mean the customer is always right). Furthermore all the problems occurring in the value creation are defined and solved together. Co-creation can finally also lead to a greater variety of products/experiences and doesn’t necessarily end with the market placement of a “product”. Co-creation can help a lot in resolving dissatisfaction of the consumers in regard to certain products or services [1].
What advantage does it bring compared with more traditional decision support processes?
Compared to traditional decision support processes co-creation process actively involves more stakeholders and can consequently identify more valuable points needed for decision making. By involving more people the amount of dissatisfaction about the final product can be lowered significantly [1].
What is the role of a facilitator, and what skills do they need?
Facilitator helps the client to structure and define the problems in specific situations and to support the problems evaluation process and development of future plans. Facilitators support can be especially helpful in resolving complex situations. Four main facilitators skills are:
- active listening,
- chart-writing,
- managing group dynamics and power shifts, and
- research closure.
Active listening is describing the ability of the modeller to clarify, develop, summarise and refine participants’ contributions. Active listening and consequent guidance of the discussion can help in avoiding blind spots, keeping track of the discussion, clarifying, getting to common grounds etc. Chart writing is needed especially if no computer support is used. It considers the appropriate writing style and speed of writing and the use of different symbols to represent the information. Managing group dynamics and power shifts is the most important facilitators skill. Difficult group situations can be managed by the facilitator in different ways. One of the most typical ones is to help the group to step back from the content and to focus more on the process. Facilitator needs to identify when in modelling he needs to intervene. Reaching closure skill helps the participants of the group to reach agreements. Facilitator must identify when the discussion about the topic is extensive enough to draw appropriate conclusions. Facilitator may also need to check if the conclusions are sufficent for those with decision making power or if more discussion is necessary [2].
References
Homework 4
ASSESSMENT OF CLIMATE CHANGE ADAPTATION STRATEGY IN SINGAPORE
Scope
Question
Assessment aimes to critically assess the adaptation strategies to climate change in Singapore. Some questions the assessment aims to answer are:
- Do the climate change adaptation strategies cover the major areas affected by the climate change?
- Do they identify the actions needed in the specific areas?
- Are effects of the adaptation strategies realistic and sufficient to efficiently combat the climate change effects?
- Are the views or opinions of all the stakeholders considered equally in the adaptation strategy?
Intended use and users
Assessment is made for all involved in managing the effects of climate change in Singapore as well as for all that could possibly be affected by the effects of climate change.
It is especially useful for decision makers, who can use the information derived from this assessment for further development, improvement and implementation of climate change adaptation strategies
Participants
Independent organisation/working group would need to be created for the assessment purposes – it will be responsible to include other participants eg:
- The Singapore Government
- Citizens of Singapore
- Different working groups: A multiagency Resilience Working Group (RWG) under the auspices of the Inter-Ministerial Committee on Climate Change (reviewing existing measures and developing new measures for adaptation to climate change), Meteorological Service Singapore, local research institutions (working on climate change models and coastal protection) - eg. Centre for Climate Research Singapore (CCRS) established by The Meteorological Service Singapore (MSS), the University of Singapore (NUS) and Nanyang Technological University (NTU) have established the following research institutes/centres: The Singapore-Delft Water Alliance (SDWA), Tropical Marine Science Institute (TMSI), Earth Observatory of Singapore (EOS), Institute of Catastrophe Risk Management (ICRM), Maritime Research Centre (MRC), NTU-JTC Industrial Infrastructure Innovation (NTU-JTC I3) Centre; Modelling and simulation is also done by the Institute of High Performance Computing (IHPC) of the Agency of Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR).
- Other stakeholders
Boundaries
Geographically the assessment is limited by the borders of Singapore.
Decisions and scenarios
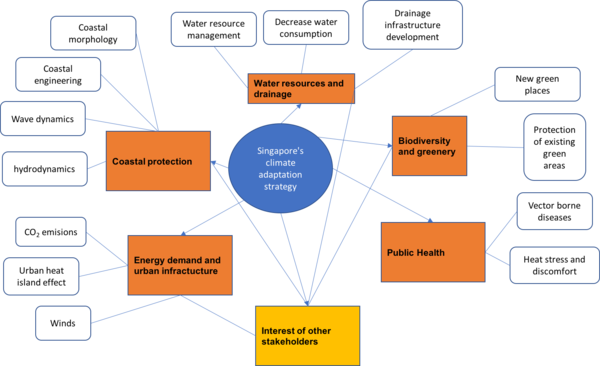
Singapore's adaptation strategy identifies 5 main areas needing action. These are presented in the table.
| Adaptation area | Description |
|---|---|
| Coastal protection | Since rising sea level poses a great threat to Singapore, the coastal protection is of great concern and includes different fields: coastal engineering, wave dynamics, coastal morphology and hydrodynamics. A Risk map study will help with identification of riskier areas and aid in developing different protection strategies of the coastline. A mangrove restoration project is also a suitable option for the creation of a buffer zone in extreme weather condition. |
| Water resources and drainage | Water resource management could become a problem in case of increased rainfall and variable weather conditions. Ensuring a sustainable water supply will be possible through four national taps: local catchment water, imported water from Malaysia, NEWater and desalinated water. NEWater refers to used water that undergoes a treatment process with an advanced dual membrane system and UV purification technologies for the purpose of replacing the need for drinking water in different processes (manufacturing, air-conditioning cooling towers etc.). It was estimated that 2/3 of water demand in Singapore will be replaced by NEWater and desalinated water.
By raising public awareness and introducing other measures, the daily per capita water consumption has already been decreased, however, since water conservation is important, the goal is to decrease the consumption even further. Developing drainage infrastructure, the flood prone areas will be reduced remarkably. |
| Biodiversity and greenery | Since animal and plant biodiversity will be affected by climate change, Singapore has given great priority in necessary green spaces in the city: extensive tree planting by the roads which decreases temperature in the near areas also parks provide an escape in urban hot temperatures. The species planted in green areas will gain more attention as well as the protection of existing ones by making sure that there are regular checks provided on already existing species. |
| Public health | Rising temperatures can be linked to increase of vector-borne disease such as dengue. In order to minimize the dengue incidence by supressing mosquito population National Environment Agency (NEA) has prepared a programme considering mosquitos, virus and human surveillance and public education and participation, law enforcement and research.
Increased occurrence of heath stress and discomfort (especially among elderly and sick) is also identified as outcomes of more frequent and severe episodes of warm weather. In collaboration with the Ministry of Health NEA will study the relationship between public health risks and climatic factors. The study will also consider forecasting different disease transmission risks in different scenarios. |
| Energy demand and urban infrastructure | Singapore may experience higher the increase in temperatures not only because of climate change but also because of urban heat island effect.
Although Singapore has energy generation capacity to meet increasing demands due to increased use of air conditioning it is important to consider the increase in carbon emissions because of increased energy production. Climate change may also affect the winds. The initial phase of the Climate Change Study found that the wind speeds in future should not be higher than the current ones, which means that the structural integrity of the buildings is unlikely to be affected. Future steps include optimal land use planning and urban design which can help to create cooler environments for people and thus counteract some of the effects of increased temperatures. The Energy Market Authority and Building and Construction Authority are responsible for studying Singapore's urban temperature profile and energy consumption in order to understand the effect of temperature increase and wind changes. Urban Redevelopment Authority is working with HDB, NUS and IHPC of A*STAR on a Climatic Mapping Study to find out the effect of built environment and urban greenery on micro-climate to identify hot spots and cooler areas in Singapore and to give recommendations on future planning and design of buidlings and public areas. |
Timing
Assessment should be conducted over a period or several periods covering the timescale of different adaptation projects. The Assessment should provide sufficient information even before the end of an adaptation project – enabling improvements in the adaptation plan. Secondly the assessment of each project of the adaptation strategy would need to be performed after its end and should consider long-lasting effects of the project. Finally the overall assessment of all the performed actions would need to be performed – this should be done regularly from the start of the adaptation projects and regularly updated with new projects and their outcomes.
The assessment of the Singapore's adaptation approach could therefore fit into the Resilience framework devised by the Singapore government to guide the efforts to safeguard Singapore against climate change effects over the next 50 to 100 years.
Answer
Results
Results of the assessment should be presented for each specific area of the adaptation and as a summary of all concerned areas.
Conclusions
Conclusions should summarize the main advantages and deficiencies of the adaptation strategy programe in each area of adaptation actions. Furthermore possible areas of imporvement may be identified.
Rationale
CAUSAL DIAGRAM
Stakeholders
- The Singapore Government
- Different community stakeholder groups:
- homes,
- schools,
- grassroots organisations,
- corporate organisations and
- private individuals.
- Different enterprises and organisation
Dependencies
Dependencies are described with the help of causal diagram. Different areas identified in the adaptation strategy need to consider different endpoints. For example in the Coastal protection coastal morphology, coastal engineering, wave dynamics and hydrodynamics are endpoints of interests. Coastal protection may also be of interest to other stakeholders due to the importance to tourism, biodiversity protection etc.
Analyses
The analysis should include different aspects/models of different scenarios, taking into account the benefits of each. Eg. Is it more beneficial to invest a lot of money in mangrove restoration or will the coastal protection need other measure that are more beneficial in the end? Also, more different aspect should be included in each decision such as all the health benefits of the population if a measure is taken etc. The analyses should help in decision making process when deciding the cost-benefit options between the measures taken.
Keywords
Singapore, adaptation, climate change, assessment
References
Climate change in Singapore [1]
Related files
Homework 5
Homework done in a pair. See page of Tamara