Macroeconomics: Difference between revisions
Iranjon 95 (talk | contribs) (Created page with "Category: Online Modelling {{assessment|moderator=Jouni Tuomisto}} {{summary box |question = What is Macro economic Model? How to use this method in practice? |answer= giv...") |
Iranjon 95 (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
*'''Global economic system. In macro economic analysis''', it is emphasized that a nation's economy is a part of a global economic system. A good or weak performance of a nation's economy can affect the performance of the world economy as a whole. | *'''Global economic system. In macro economic analysis''', it is emphasized that a nation's economy is a part of a global economic system. A good or weak performance of a nation's economy can affect the performance of the world economy as a whole. | ||
=== | ===Demand & Supply=== | ||
The Analysis of supply and demand shows how a market mechanism solves the three problems of ''what'', ''how'' and ''for whom''. A market blends together demands and supplies. Demand comes from consumers and who are spreading their dollars votes among available goods and services, while business supply the goods and services with the goal of maximizing their profit. | |||
'''A. The Demand Schedule''' | |||
* A demand schedule shows the relationship between the quantity demanded and the price of a commodity other things held constant. Such a demand schedule, depicted graphically by a demand curve, holds constant other thing like family income, tastes and the price of other goods. Almost all commodities obey the ''law of downward-sloping demand'', which hold that quantity demanded falls as a good's price rise. this law is represented by a downward-sloping demand curve. | |||
* Many influence lie behind the demand schedule for the market as a whole: average family incomes, population, the prices of related goods, tastes, and special influence. When these influences change, demand curve will shift. | |||
'''B.The Supply Schedule''' | |||
* The supply schedule (or supply curve) gives the relationship between the quantity of a good that producers desire to sell- other things constant- and that good's price. Quantity supplied generally responds positively to price, so the supply curve will be upward sloping. | |||
* Element other than the good's price affect its supply. The most important influence is the commodity's production cost, determined by the state of technology and by input prices. other elements in supply include the prices of related goods, government policies and special influence. | |||
===Boundaries=== | ===Boundaries=== | ||
Revision as of 13:36, 31 January 2012
| [show] |
|---|
| Main message: |
|---|
| Question:
What is Macro economic Model? How to use this method in practice? given current knowledge, Macroeconomics is the study of the behavior of the economy as a whole. It examines the forces that affect many firm, consumer and workers at the same time. |
Scope
The importance/issues/scope, which are addressed in macro economics are in brief as under:
- It helps in understanding the determination of income and employment. Late J.M. Keynes laid great stress on macro economic analysis. He, in his revolutionary book, "General Theory, Employment interest and Money", brought drastic changes in economic thinking. He explained the forces or factors which determine the level of aggregate employment and output in the economy.
- 'Economic growth: The macro economic models help us to formulate economic policies for achieving long run economic growth with stability. The new developed growth theories explain the causes of poverty in under developed countries and suggest remedies to overcome them.
- Determination of general level of prices. Macro economic analysis answers questions as to how the general price level is determined and what is the importance of various factors which influence general price level.
- Income shares from the national income. Mr. M. Kalecki and Nicholas Kelder, by making departure from Ricardo theory, has presented a macro theory of distribution of income. According to these economists, the relative shares of wages and profits depend upon the ratio of investment to national income.
- Global economic system. In macro economic analysis, it is emphasized that a nation's economy is a part of a global economic system. A good or weak performance of a nation's economy can affect the performance of the world economy as a whole.
Demand & Supply
The Analysis of supply and demand shows how a market mechanism solves the three problems of what, how and for whom. A market blends together demands and supplies. Demand comes from consumers and who are spreading their dollars votes among available goods and services, while business supply the goods and services with the goal of maximizing their profit.
A. The Demand Schedule
- A demand schedule shows the relationship between the quantity demanded and the price of a commodity other things held constant. Such a demand schedule, depicted graphically by a demand curve, holds constant other thing like family income, tastes and the price of other goods. Almost all commodities obey the law of downward-sloping demand, which hold that quantity demanded falls as a good's price rise. this law is represented by a downward-sloping demand curve.
- Many influence lie behind the demand schedule for the market as a whole: average family incomes, population, the prices of related goods, tastes, and special influence. When these influences change, demand curve will shift.
B.The Supply Schedule
- The supply schedule (or supply curve) gives the relationship between the quantity of a good that producers desire to sell- other things constant- and that good's price. Quantity supplied generally responds positively to price, so the supply curve will be upward sloping.
- Element other than the good's price affect its supply. The most important influence is the commodity's production cost, determined by the state of technology and by input prices. other elements in supply include the prices of related goods, government policies and special influence.
Boundaries
* Boundaries define which parts of the reality are taken into the assessment and which are excluded within
spatial, temporal and other dimensions.
Scenarios
* Scenarios define particular conditions that are of interest irrespective whether they describe
reality or not (e.g. what-if scenarios).
Intended users
* Intended users are those for whom the assessment is made.
Participants
* Participants are those who may participate in the making of the assessment.
The minimum group of people for a successful assessment is always described.
If some groups must be excluded, this must be explicitly motivated.
Definition
Upload a causal diagram and change the right name here.
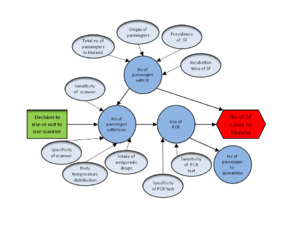
Decision variables
* Decision variables: decisions that are considered.
Indicators
* Indicators: outcome variables of interest.
Value variables
* Value variables: value judgements (usually about indicators).
Other variables
* Other variables: any variables that link to the causal network and are within the boundaries of the assessment.
Analyses
* Analyses: statistical and other analyses that contain two or more variables, e.g. optimizing.
Indices
* Indices: lists of particular locations along spatial, temporal, or other dimensions.
Result
* Results of indicators and assessment-specific analyses.
Results
Conclusions
* Conclusions are based on the results, given the scope.