Risk assessment of nitrate in drinking water: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
* BAU (business-as-usual) | * BAU (business-as-usual) | ||
For the first pass it was deemed appropriate to carry out a diagnostic assessment i.e. to estimate the scale of the health impacts under present conditions, which in this case make use of 2001 as the baseline year. It was recognised that the causal diagram should be constructed in such a way that the introduction of policy scenarios is possible, since this is intended for the second pass of the assessment. The introduction of such potential policy scenarios would allow the diagnostic assessment to be transformed into a prognostic assessment i.e. a causal diagram which allows the estimation the likely consequences of different policy options, primarly as a basis for choosing between them. <ref name="briggs">Briggs DJ. Integrated assessment for policies on environmental health. Draft. Unpublished document. 2008. | |||
</ref> | |||
=== Intended users === | === Intended users === | ||
Revision as of 07:19, 9 June 2008
This is the main page of nitrate risk assessment conducted in INTARESE WP3.4. The analytica file can be uploaded here: File:Nitrate.ANA
Scope
Purpose
To investigate the effects of nitrate contaminated drinking water.
Boundaries
- European countries in selected regions:
- Finland
- Romania
- Spain
- UK
- Infants < 6 months of age
- Exposure to nitrate via baby food formula mixed with drinking water
- Effects: infant methemoglobinemia
Scenarios
- BAU (business-as-usual)
For the first pass it was deemed appropriate to carry out a diagnostic assessment i.e. to estimate the scale of the health impacts under present conditions, which in this case make use of 2001 as the baseline year. It was recognised that the causal diagram should be constructed in such a way that the introduction of policy scenarios is possible, since this is intended for the second pass of the assessment. The introduction of such potential policy scenarios would allow the diagnostic assessment to be transformed into a prognostic assessment i.e. a causal diagram which allows the estimation the likely consequences of different policy options, primarly as a basis for choosing between them. [1]
Intended users
Participants
- Researchers at KTL
- Researcher at Imperial College London
- Researchers at London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine
- Researchers at Municipal Institute of Medical Research Foundation
Definition
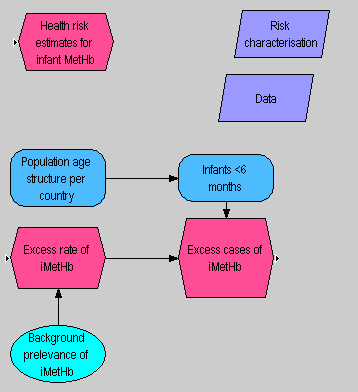
Causal diagram
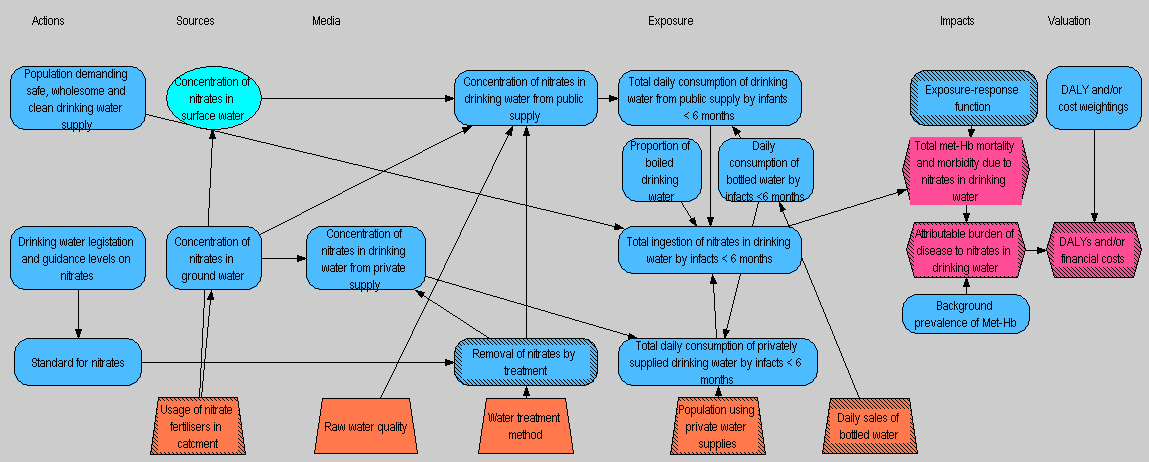
Causal diagram of nitrate risk assessment
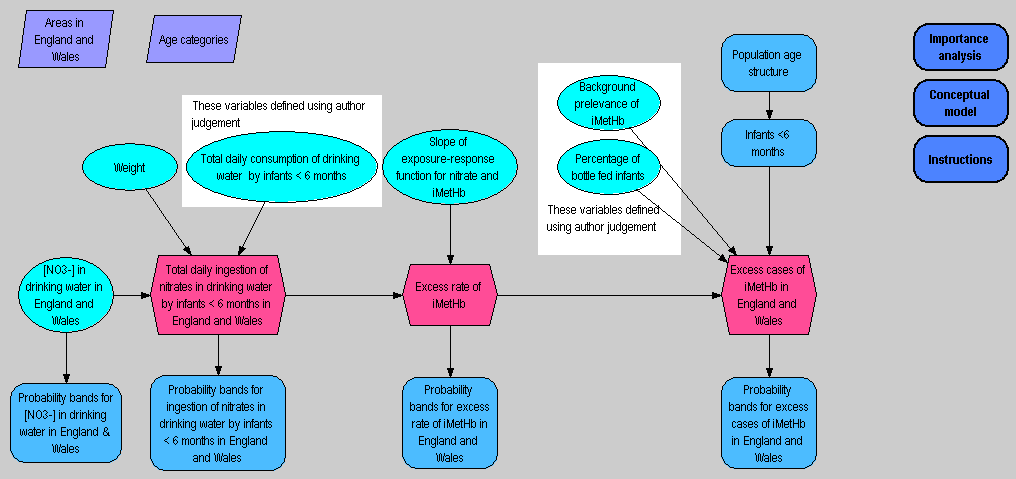
Model of nitrate risk assessment
Decision variables
- Water source (population using private water supplies)
Indicators
- Total MetHg morbidity and mortality due to nitrate in drinking water
- Nitrate/MetHg DALYs
Other variables
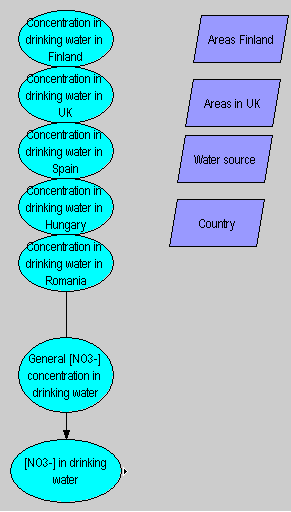
- Concentration of nitrate in drinking water from public supply
- Concentration of nitrate in drinking water from private supply
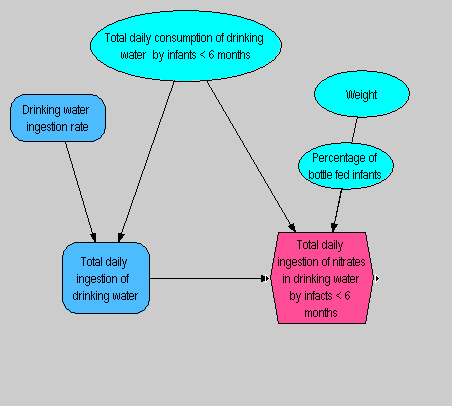
- Exposure of infants < 6 months to water from private supply
- Infection status of infants < 6 months
Modules
Sources of nitrate in drinking water
'
Exposure to nitrate in drinking water
Health effects of nitrate in drinking water
Analyses
Result
Results
Conclusions
- ↑ Briggs DJ. Integrated assessment for policies on environmental health. Draft. Unpublished document. 2008.