Epidemiological modelling: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
m (→Rationale) |
||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
To assess the sensitivity of the predictions produced by the epidemiological model, | To assess the sensitivity of the predictions produced by the epidemiological model, | ||
effects of some alternative scenarios regarding the role of certain serotypes in PCV10 and PCV13 were calculated. | effects of some alternative scenarios regarding the role of certain serotypes in PCV10 and PCV13 were calculated. | ||
The | In particular, the scenarios concern assumptions about direct and/or indirect protection against serotype 3 in PCV13, | ||
against serotype 6A in PCV10, and against 19A in PCV10. The detailed results are reported on a separate page: [[Sensitivity_analysis_pcv_model]]. In summary, the most influential assumptions are whether or not there will be population-level impact on serotype 3 disease under PCV13 and serotype 6A disease under PCV10. | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
Revision as of 05:36, 21 August 2014
| Moderator:Nobody (see all) Click here to sign up. |
|
|
| Upload data
|
In Opasnet many pages being worked on and are in different classes of progression. Thus the information on those pages should be regarded with consideration. The progression class of this page has been assessed:
|
This page needs a curator. Learn more about curating Opasnet pages. |
Question
How to predict the net effectiveness of pneumococcal conjugate vaccination with a given set of serotypes when the vaccine is included in the national immunisation programme?
- The focus is on the incidence of invasive pneumococcal disease (IPD) cases in different age groups covering the whole population.
- The model is assumed to be valid in a population in which pneumococcal conjugate vaccination of infants has been in place for several years so that a new steady-state after vaccination has been reached.
- The coverage of vaccination and vaccine efficacy against carriage are assumed to be high enough to justify the assumption of complete elimination of vaccine-type carriage among both the vaccinated and also, due to substantial herd effects, among the unvaccinated members of the population.
- Vaccine-type carriage will be completely replaced by carriage of the non-vaccine types whose disease causing potential is not altered by vaccination.
Answer
The predicted reduction in the incidence of invasive pneumococcal disease (IPD) in different age groups are obtained from the serotype replacement model (Nurhonen and Auranen, 2014).
Rationale
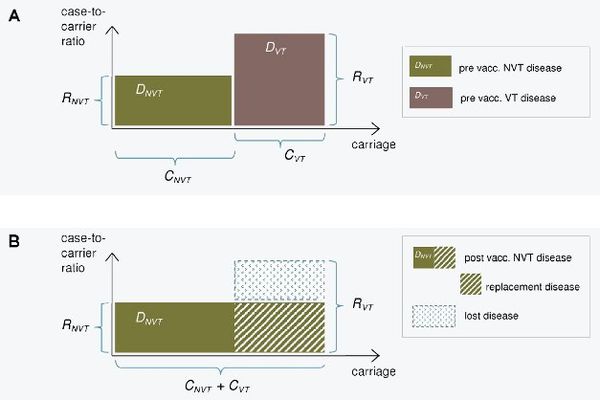
The epidemiological model for pneumococcal carriage and disease is based on the assumption that vaccination completely eliminates vaccine-type carriage in the vaccinated population and that vaccine-type carriage is completely replaced by non-vaccine-type carriage. The implications of this replacement on the decrease or increase in pneumococcal disease then depend on the disease causing potential of the replacing types compared to that of the replaced types. To predict the incidence of post-vaccination disease only pre-vaccination data on serotype-specific carriage and disease are used.
The consequences of serotype replacement in the model depend on two key assumptions regarding the new steady-state after vaccination:
- the relative serotype proportions among the non-vaccine types are not affected by vaccination (proportionality assumption);
- the case-to-carrier ratios (the disease causing potentials) of individual serotypes remain at their pre-vaccination levels.
The implications of vaccination on disease incidence are assumed to be solely due to the elimination of vaccine type carriage and its replacement by non vaccine-type carriage. An exception to this is when protective efficacy against disease without any efficacy against carriage is assumed for certain serotypes (a feature to be added).
Related research
The replacement model was built to reflect the accumulated 15 year long experience on use of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines worldwide and the related scientific research activity. Some of the most recent relevant publications are listed on a separate page: References.
Sensitivity analysis
To assess the sensitivity of the predictions produced by the epidemiological model,
effects of some alternative scenarios regarding the role of certain serotypes in PCV10 and PCV13 were calculated.
In particular, the scenarios concern assumptions about direct and/or indirect protection against serotype 3 in PCV13,
against serotype 6A in PCV10, and against 19A in PCV10. The detailed results are reported on a separate page: Sensitivity_analysis_pcv_model. In summary, the most influential assumptions are whether or not there will be population-level impact on serotype 3 disease under PCV13 and serotype 6A disease under PCV10.
Computation
The following program illustrates the working of the replacement model. In its current implementation the code allows the user to specify 4 vaccine compositions and then displays the predicted number of IPD cases in Finland per year corresponding to these vaccines. The results are shown by serotype and by age category (<5 and 5+ year olds). Possible choices for vaccine compositions are: PCV10, PCV13, no vaccination and a user specified serotype composition. The program is based on the code in File S1 of Nurhonen and Auranen, 2014.
Instructions for user: Choose the desired vaccine compositions from the list below and then press "Run code".
You can compare 2,3 or 4 vaccine compositions. The results will be displayed on a separate tab. The default choice is PCV10 and PCV13.
Data
| Show details | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Initiate functions
See also
References
Comment the content