Societal context of assessments: Difference between revisions
(some stuff from related pages copied here) |
(Template:Publication added) |
||
| (12 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{encyclopedia| | [[Category:Open assessment]] | ||
{{encyclopedia|moderator=Mikko Pohjola | |||
| reference = {{publication | |||
| authors = Mikko V. Pohjola | |||
| page = Societal context of assessments | |||
| explanation = | |||
| publishingyear = 2010 | |||
| urn = | |||
| elsewhere = | |||
}} | |||
}} | |||
The basic idea in | The basic idea in all practice of scientific assessment, be it risk, impact, integrated, health impact, integrated environmental health impact, or whatever assessment, is to use the means and methods of science to support societal decision making. Assessments aim to prevent random decision making, as in [[flipism]], but also decisions based on incomplete, biased or false information, as well as decisions founded on societally unacceptable values, especially when these decisions address matters of significant societal importance. They are thus processes of collecting and synthesizing knowledge and values from plural sources as solutions to societal problems. | ||
In principle, the whole endeavor of assessment could be considered as an interface between science and society, as an institutionalization of using the best available knowledge to guide societal actions, although the current assessment practice usually turns out as something quite different. Assessments are often perceived as scientific, or at least science-based, activity but unlike science according to the traditional ideal, assessments do not only search for the truth, but also serve practical, instrumental purposes. E.g. for the purpose of assessment method development, it is important to understand that assessments are intentional activities of producing artifacts with instrumental functions. Assessments could be considered as simultaneously serving two masters; the scientific quest for truth and the practical needs of the society. Balancing between the forces of two masters makes the practice of assessment even more challenging. Assessments can also be triggered by needs arising from different aspects. There can be problem-driven assessments where the assessment questions are formulated according to practical societal needs. There can also be exploratory assessments that rather generate and evaluate questions that could be answered with an assessment (model). | |||
'''Asessments in environment and health | |||
Here assessments are considered in relation to the field of environmental health, for example as integrated environmental health impact assessments (IEHIA). The concept of assessment adopted here is however generalizable to virtually any field of science-based support of societal decision making. Environmental health assessment (EHA) is an endeavor of analyzing relations between environmental phenomena and human health for the purpose of informing societal decision making on issues relevant to environment and health. It takes place on the interface between science and society, attempting to bridge the practical needs of society with the knowledge creating processes of science. As both environment and health are very broad concepts, intertwined with many aspects of human society, EHA is by its nature a multi-disciplinary field of practice that addresses issues of interest to many different organizations and individuals with different societal roles and perspectives. Naturally this includes all the scientific experts appointed to make the assessment task and the policy makers having an obligation to deal with the particular issue at hand, but also representatives of industry and commerce, NGO's and the general public e.g. as consumers or citizens. EHA can thus be perceived as a science-based activity that takes place on the interface between science and society, bridges scientific knowledge and practice with the practical needs of e.g. policy, business and everyday life, thereby providing enlightenment and increased awareness within the society at large. | |||
The term assessment is often used interchangeably to refer to either the process of making an assessment (assessment process) or the output of that process (assessment product). This confusion is not only a terminological one, but it appears that the actual concepts of producing information, as e.g. in an assessment process, and the information produced, as e.g. an assessment product, are often confused. Another essential aspect related to assessments as societal endeavors of generating solutions to practical problems that is far too often neglected is the use of assessment products. The general assessment framework describing the relationships between assessment process, assessment product and use of assessment product is illustrated in the figure below. | |||
[[Image: | [[Image:Assessment push and pull.PNG|center|General assessment framework]] | ||
Assessments can be considered as an institutionalization of intentional activities of informing societally relevant decisions. Assessment is a means (informing) to an end (decision), not an end in itself. To put in another way, without proper use of the assessment product, the whole process of assessment is completely futile. Thus, [[Assessment|assessments]] should always be done for a purpose. When the purpose is identified and kept clear in mind and preferably explicated and made public, it helps to guide the process in producing a desired kind of assessment product. The general purpose is to improve societal decision making by providing good descriptions of chosen parts of reality for use in decision making, but the specific purpose statement for a particular assessment must be far more detailed. Proper identification of the purpose of assessment crucially affects the assessment process, the content and essence of the final product, and consequently the outcome of using the product in decision making (see figure below). | |||
[[Image:RA-SH chain.PNG|center|The chain from assessment to societal consequences]] | |||
The whole endeavor of assessment should be driven by the knowledge need of the society and it should be deeply integrated in the overall process of decision making upon societally important matters. There are several more specific assessment frameworks that bound the objects of assessment to certain particular topics, and accordingly the methods of assessment to meet the specific needs of these topics, e.g. chemical risk assessment (RA, risks of chemicals), environmental impact assessment (EIA, impacts to the environment) and integrated environmental health impact assessment (IEHIA, impacts of environmental phenomena to human health). The general assessment framework, however, addresses the role of assessment in between science and society, or using science to serve the needs of society. The idea of assessment practice is not relevant only within a specific context, but also more broadly as a general societal activity, in particular in operationalising large structural changes to existing systems. This is crucial for example when considering the needs to adapt societal structures and practices in the face of the global climate change. In order to make this possible, the whole endeavor of assessment must be considered as a process of systematic social learning and facilitation of social innovations. | |||
== References == | |||
<References/> | |||
== See also == | |||
* [[General assessment framework]] | |||
* [[Purpose]] | |||
* [[Assessments - science-based decision support]] | |||
* [[Operationalising large structural changes to existing systems]] | |||
* [[Influencing environmental decisions of authorities, and responding to that]] | |||
* [[Innovation and research]] | |||
* | * [[Flipism]] | ||
* | [[Category:THL publications 2009]] | ||
* | [[Category:THL publications 2010]] | ||
* | |||
* | |||
Latest revision as of 06:40, 30 January 2011
This page is a encyclopedia article.
The page identifier is Op_en2083 |
|---|
| Moderator:Mikko Pohjola (see all) |
|
|
| Upload data
|
The basic idea in all practice of scientific assessment, be it risk, impact, integrated, health impact, integrated environmental health impact, or whatever assessment, is to use the means and methods of science to support societal decision making. Assessments aim to prevent random decision making, as in flipism, but also decisions based on incomplete, biased or false information, as well as decisions founded on societally unacceptable values, especially when these decisions address matters of significant societal importance. They are thus processes of collecting and synthesizing knowledge and values from plural sources as solutions to societal problems.
In principle, the whole endeavor of assessment could be considered as an interface between science and society, as an institutionalization of using the best available knowledge to guide societal actions, although the current assessment practice usually turns out as something quite different. Assessments are often perceived as scientific, or at least science-based, activity but unlike science according to the traditional ideal, assessments do not only search for the truth, but also serve practical, instrumental purposes. E.g. for the purpose of assessment method development, it is important to understand that assessments are intentional activities of producing artifacts with instrumental functions. Assessments could be considered as simultaneously serving two masters; the scientific quest for truth and the practical needs of the society. Balancing between the forces of two masters makes the practice of assessment even more challenging. Assessments can also be triggered by needs arising from different aspects. There can be problem-driven assessments where the assessment questions are formulated according to practical societal needs. There can also be exploratory assessments that rather generate and evaluate questions that could be answered with an assessment (model).
Asessments in environment and health
Here assessments are considered in relation to the field of environmental health, for example as integrated environmental health impact assessments (IEHIA). The concept of assessment adopted here is however generalizable to virtually any field of science-based support of societal decision making. Environmental health assessment (EHA) is an endeavor of analyzing relations between environmental phenomena and human health for the purpose of informing societal decision making on issues relevant to environment and health. It takes place on the interface between science and society, attempting to bridge the practical needs of society with the knowledge creating processes of science. As both environment and health are very broad concepts, intertwined with many aspects of human society, EHA is by its nature a multi-disciplinary field of practice that addresses issues of interest to many different organizations and individuals with different societal roles and perspectives. Naturally this includes all the scientific experts appointed to make the assessment task and the policy makers having an obligation to deal with the particular issue at hand, but also representatives of industry and commerce, NGO's and the general public e.g. as consumers or citizens. EHA can thus be perceived as a science-based activity that takes place on the interface between science and society, bridges scientific knowledge and practice with the practical needs of e.g. policy, business and everyday life, thereby providing enlightenment and increased awareness within the society at large.
The term assessment is often used interchangeably to refer to either the process of making an assessment (assessment process) or the output of that process (assessment product). This confusion is not only a terminological one, but it appears that the actual concepts of producing information, as e.g. in an assessment process, and the information produced, as e.g. an assessment product, are often confused. Another essential aspect related to assessments as societal endeavors of generating solutions to practical problems that is far too often neglected is the use of assessment products. The general assessment framework describing the relationships between assessment process, assessment product and use of assessment product is illustrated in the figure below.
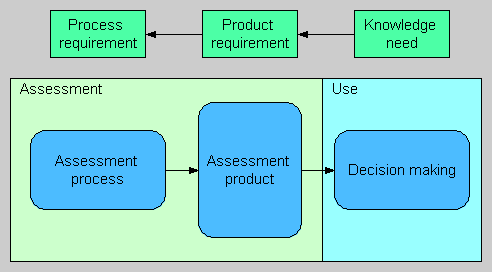
Assessments can be considered as an institutionalization of intentional activities of informing societally relevant decisions. Assessment is a means (informing) to an end (decision), not an end in itself. To put in another way, without proper use of the assessment product, the whole process of assessment is completely futile. Thus, assessments should always be done for a purpose. When the purpose is identified and kept clear in mind and preferably explicated and made public, it helps to guide the process in producing a desired kind of assessment product. The general purpose is to improve societal decision making by providing good descriptions of chosen parts of reality for use in decision making, but the specific purpose statement for a particular assessment must be far more detailed. Proper identification of the purpose of assessment crucially affects the assessment process, the content and essence of the final product, and consequently the outcome of using the product in decision making (see figure below).
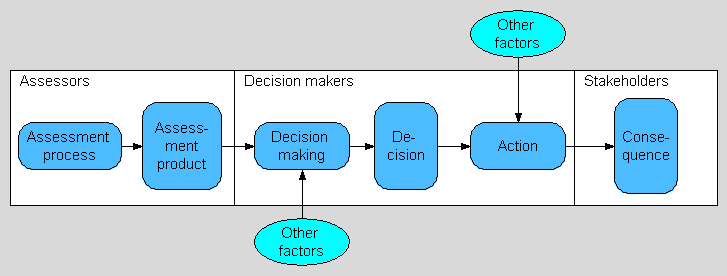
The whole endeavor of assessment should be driven by the knowledge need of the society and it should be deeply integrated in the overall process of decision making upon societally important matters. There are several more specific assessment frameworks that bound the objects of assessment to certain particular topics, and accordingly the methods of assessment to meet the specific needs of these topics, e.g. chemical risk assessment (RA, risks of chemicals), environmental impact assessment (EIA, impacts to the environment) and integrated environmental health impact assessment (IEHIA, impacts of environmental phenomena to human health). The general assessment framework, however, addresses the role of assessment in between science and society, or using science to serve the needs of society. The idea of assessment practice is not relevant only within a specific context, but also more broadly as a general societal activity, in particular in operationalising large structural changes to existing systems. This is crucial for example when considering the needs to adapt societal structures and practices in the face of the global climate change. In order to make this possible, the whole endeavor of assessment must be considered as a process of systematic social learning and facilitation of social innovations.
References