Benefit-risk assessment of fish consumption for Beneris
| Moderator:Olli (see all) |
|
|
| Upload data
|
Contents
Scope
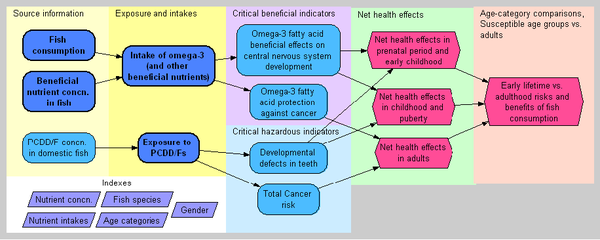
Net health effects of fish consumption due to intake of beneficial nutrients and constituents and on the other hand, exposure to environmental contaminants taken up by fish. D↷
Boundaries
- Environmental contaminants relevant from the human health point of view and thus included in the assessment are:
- polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans (PCDD/F),
- polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB),
- mercury as methyl mercury (MeHg),
- Nutritional constituents relevant from the human health point of view include a wide variety of effects and can be viewed from Benefit-risk assessment of fish and related policy options under title "Health consequences attributable to fish consumption". However, readily usable beneficial constituents with quantitative dose-response information available included in the assessment are:
- omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA): EPA and DHA,
- iodine (I),
- Health effects of fish consumption used in the assessment encompass neurological effects during early development, developmental dental defects, cardiovascular disease and cancer. In particular, the following health effects are considered:
- the effect of prenatal exposure to MeHg and omega-3 fatty acids on childhood cognitive development (IQ),
- the effect of exposure to dioxins and PCBs during early childhood on developmental dental defects (defects of enamel in permanent teeth or missing of smaller molars),
- the effect of exposure to MeHg and omega-3 fatty acids in adulthood on cardiovascular disease,
- the effect of exposure to dioxins and PCBs on cancer.
- Beneris population - the Beneris population is defined as the general population (all age groups) in
- Finland,
- Ireland,
- Spain,
- Denmark.
Current assessment is performed based on Finnish conditions only.
- Current situation (BAU)
Scenarios
BAU-type assessment (business-as-usual assessment), i.e. a burden-of-disease assessment with only one decision scenario. D↷
Intended users
Experts, researchers and decision makers in the field of environmental health, anyone interested and concerned with beneficial and hazardous constituents in fish species in the markets.
Participants
Participation basically completely open. Some parts containing original data will be protected.
- Everyone interested
- Beneris researchers (full access to the protected parts)
Definition
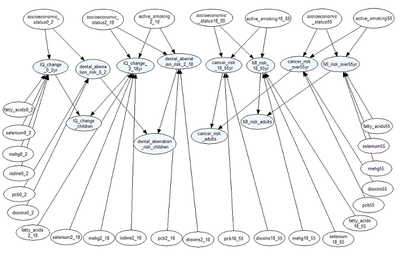
Variables
- Decision variables: None at the moment D↷
- Indicators: See health effect variables in the table below
- Other variables: See table
- Variable:Risk for dental aberrations in children
- Myocardial infarction risk in adults in Beneris
- Total cancer risk in adults in Beneris
- Intelligence quotient (IQ) in children in Beneris
---
- Cancer dose responses
- Cardiovascular dose responses
- Mental health dose-responses
- Developmental dose-responses
- All-cause mortality dose-responses
- Total cancer risks in adults
- Fish consumption in Finland, pregnant women
- Nutrients in fish species
- Exposure-response of MeHg intake vs. IQ change in children
- Exposure-response of MeHg intake for MI risk
- Exposure-response of PCB intake for cancer risk
- Exposure-response of TCDD intake for teeth defects
- Exposure-response of PCB intake for dental aberrations in children
- Exposure-response of dioxin for dental aberrations
- Generalized exposure-response for teeth defects caused by TCDD
- PCB intake from fish
- PCDD/F intake from fish
- Omega-3 fatty acid concentration is fish species
- [
| Nutritional benefits and risks of PCDD/F exposure of fish consumption in Finnish children and adults Analytica model |
| Beneris:Risk assessment of MeHg and n-3 fatty acids in fish |
Indexes
| Fish species |
|---|
|
| Nutrients |
|---|
|
Age categorizations were chosen in order to describe health effects of fish consumption in infants (0-2 years, this class includes prenatal period as well), adolescent (2-18 years), adults (18-55 years) and elderly people (55-).
| Age categories (years) |
|---|
|
Result
See also
- Fish-related assessments:
- A previous version of this assessment with important background information
- EU funded projects from Cordis database